STATS 220
🚀Factors & date-times📆
1 / 31
2 / 31
- forcats: my fav logo
- lubridate: my fav pkg name
Atomic vectors

3 / 31
Coerce to factors from one type
dept <- c("Physics", "Mathematics", "Statistics", "Computer Science")dept#> [1] "Physics" "Mathematics" "Statistics" #> [4] "Computer Science"library(tidyverse) # library(forcats)dept_fct <- as_factor(dept)dept_fct#> [1] Physics Mathematics Statistics #> [4] Computer Science#> 4 Levels: Physics Mathematics ... Computer Science4 / 31
- diff displays
- fct: w meta info
typeof(dept)#> [1] "character"class(dept)#> [1] "character"as.integer(dept)#> [1] NA NA NA NAsort(dept)#> [1] "Computer Science"#> [2] "Mathematics" #> [3] "Physics" #> [4] "Statistics"typeof(dept_fct)#> [1] "integer"class(dept_fct)#> [1] "factor"as.integer(dept_fct)#> [1] 1 2 3 4sort(dept_fct)#> [1] Physics Mathematics #> [3] Statistics Computer Science#> 4 Levels: Physics ... Computer Science5 / 31
Factors
- Factors are used to represent a categorical variable in R.
- There is a fixed and known set of possible values.
- The fixed set of values is called the levels of the factor.
dept_fct#> [1] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> Levels: Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Sciencelevels(dept_fct)#> [1] "Physics" "Mathematics" "Statistics" "Computer Science"rep(dept_fct, 3)#> [1] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> [5] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> [9] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> Levels: Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science6 / 31
Create factors
- change the base level for modelling
- display characters in a non-alphabetical order
dist_dept <- unique(dept)factor(dept, levels = dist_dept) # in first appearance order#> [1] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> Levels: Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Sciencefactor(dept, levels = rev(dist_dept)) # in reverse order#> [1] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> Levels: Computer Science Statistics Mathematics Physics7 / 31
- data values not changing, only meta info levels changed
Reorder factor levels to easily perceive patterns
sci_tbl
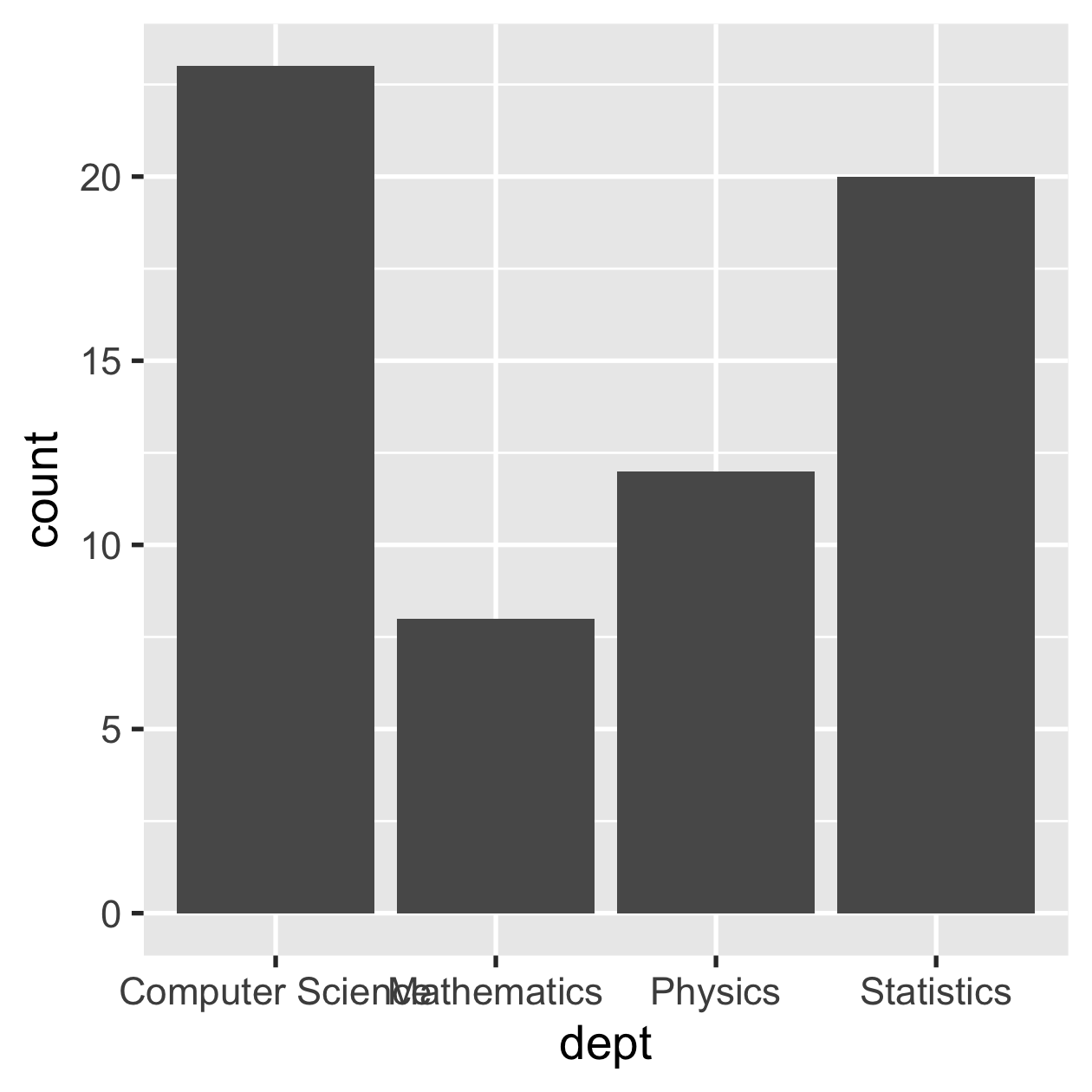

8 / 31
- in default order, takes time to process info
Reorder factor levels to easily perceive patterns
movies

9 / 31
fct_reorder() by sorting along another variable
sci_tbl %>% mutate(dept = fct_reorder(dept, count)) %>% ggplot(aes(dept, count)) + geom_col()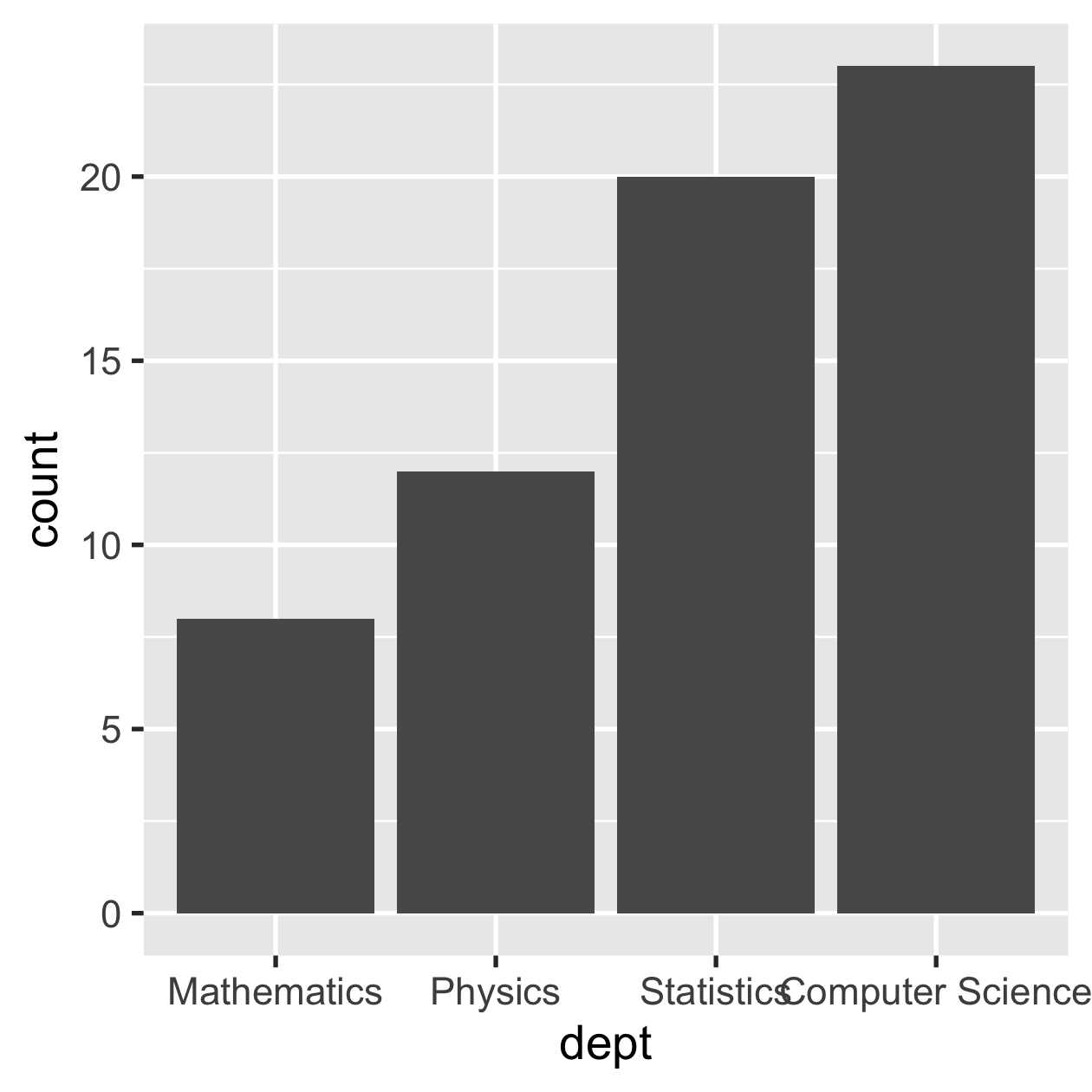
sci_tbl %>% mutate(dept = fct_reorder(dept, -count)) %>% ggplot(aes(dept, count)) + geom_col()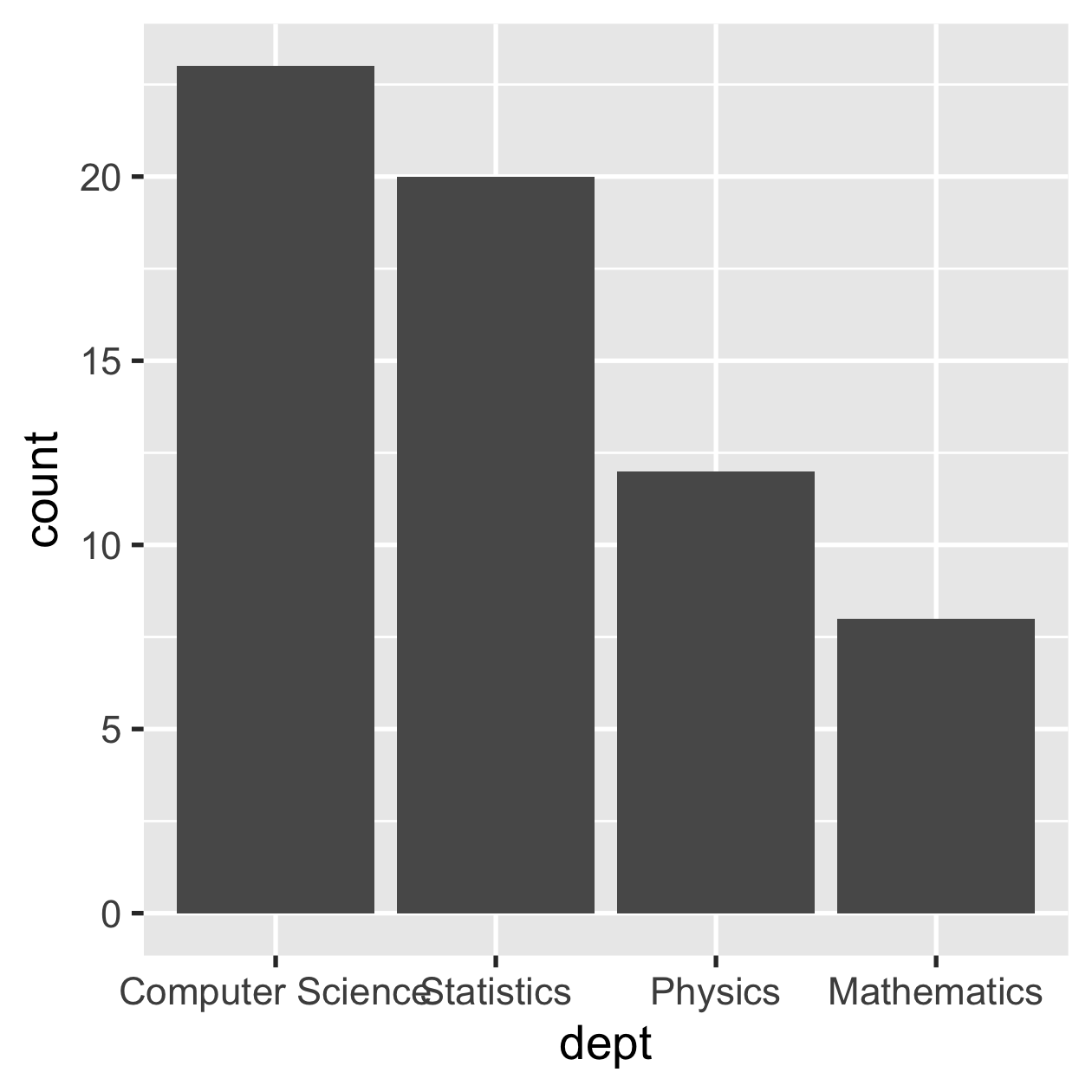
10 / 31
fct_reorder() by sorting along another variable
fct_reorder(sci_tbl$dept, sci_tbl$count)#> [1] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> Levels: Mathematics Physics Statistics Computer Sciencefct_reorder(sci_tbl$dept, -sci_tbl$count)#> [1] Physics Mathematics Statistics Computer Science#> Levels: Computer Science Statistics Physics Mathematics11 / 31
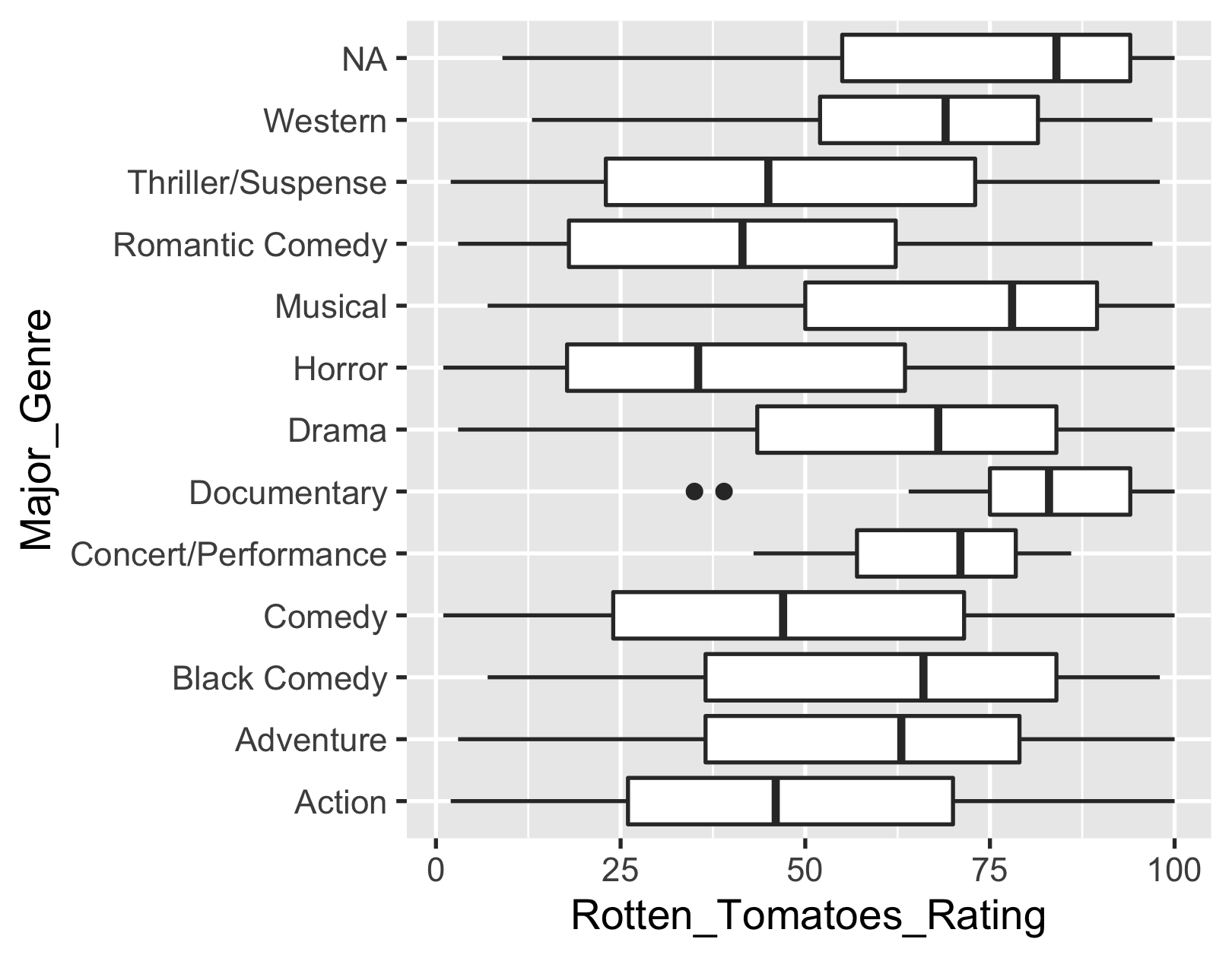
fct_reorder() by sorting along another variable with fun()
movies %>% mutate( Major_Genre = fct_reorder( Major_Genre, Rotten_Tomatoes_Rating, .fun = median, na.rm = TRUE)) %>% ggplot(aes( Rotten_Tomatoes_Rating, Major_Genre)) + geom_boxplot()
12 / 31
fct_infreq() by counting obs with each level (largest first)
movies %>% mutate(Major_Genre = fct_infreq( Major_Genre)) %>% ggplot(aes(y = Major_Genre)) + geom_bar()
13 / 31
fct_lump() by lumping together factor levels into "other"
movies %>% mutate(Major_Genre = fct_infreq( fct_lump(Major_Genre, n = 6))) %>% ggplot(aes(y = Major_Genre)) + geom_bar()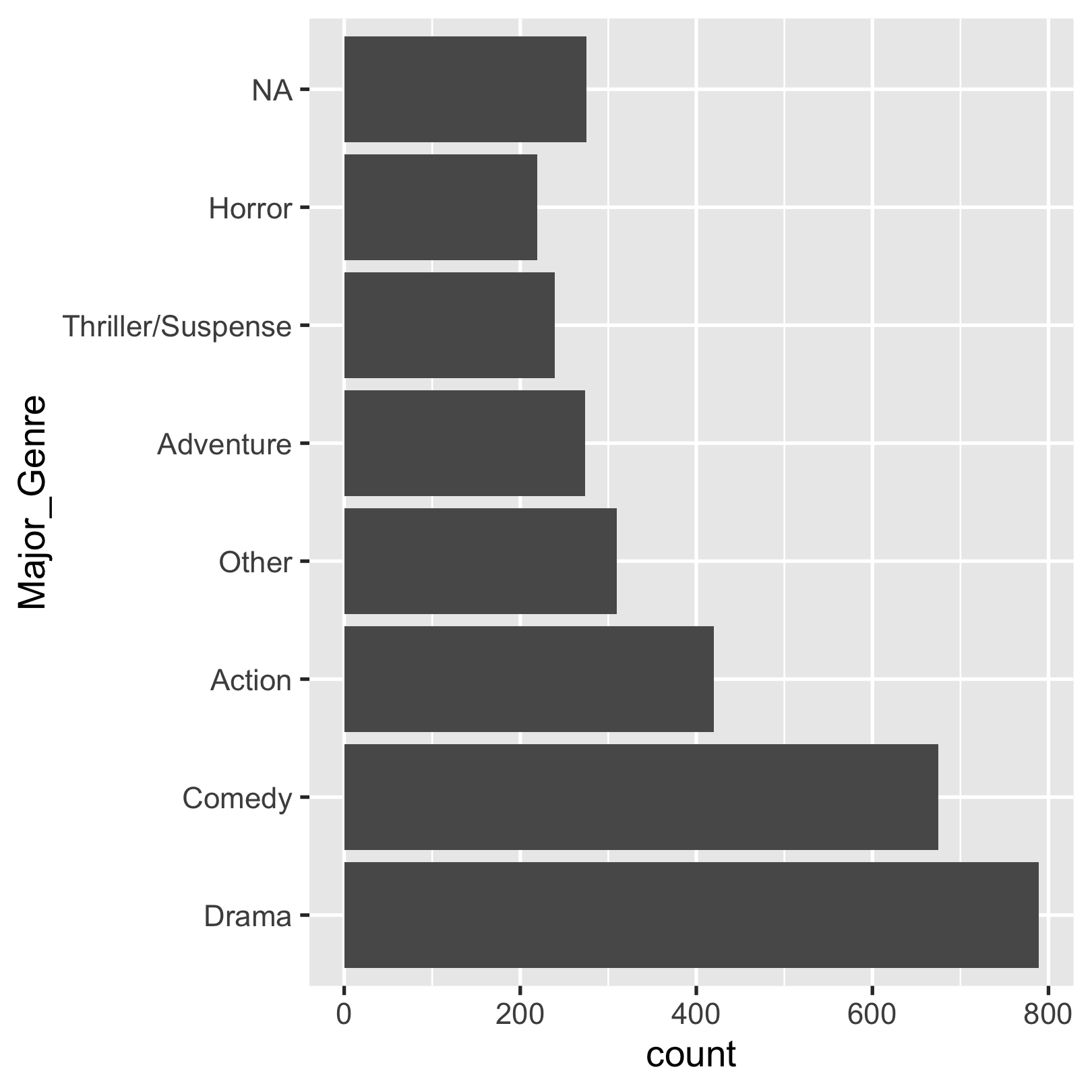
14 / 31
Convert numerics to factors: UoA grade scales
set.seed(220)scores_sim <- round( rnorm(309, mean = 70, sd = 10), digits = 2)scores_tbl <- tibble(score = scores_sim)scores_tbl#> # A tibble: 309 x 1#> score#> <dbl>#> 1 58.2#> 2 80.1#> 3 51.4#> 4 80.5#> 5 63.8#> 6 51.0#> # … with 303 more rowsscores_tbl %>% ggplot(aes(x = score)) + geom_histogram() + geom_vline(xintercept = 70, colour = "red")
15 / 31
cut() numerics to factors
(rng <- c(0, seq(39, 89, by = 5), 100))#> [1] 0 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 74 79 84 89 100scores_tbl %>% mutate(range = cut(score, breaks = rng, include.lowest = TRUE))#> # A tibble: 309 x 2#> score range #> <dbl> <fct> #> 1 58.2 (54,59]#> 2 80.1 (79,84]#> 3 51.4 (49,54]#> 4 80.5 (79,84]#> 5 63.8 (59,64]#> 6 51.0 (49,54]#> # … with 303 more rows16 / 31
- underappreciated
cut(), built-in function - include
0, but doesn't matter for this data
fct_recode() changes factor levels by hand
scores_schemes <- scores_tbl %>% mutate( range = cut(score, breaks = rng, include.lowest = TRUE), grade = fct_recode(range, # new_lvl = old_lvl "D-" = "[0,39]", "D" = "(39,44]", "D+" = "(44,49]", "C-" = "(49,54]", "C" = "(54,59]", "C+" = "(59,64]", "B-" = "(64,69]", "B" = "(69,74]", "B+" = "(74,79]", "A-" = "(79,84]", "A" = "(84,89]", "A+" = "(89,100]"))scores_schemes#> # A tibble: 309 x 3#> score range grade#> <dbl> <fct> <fct>#> 1 58.2 (54,59] C #> 2 80.1 (79,84] A- #> 3 51.4 (49,54] C- #> 4 80.5 (79,84] A- #> 5 63.8 (59,64] C+ #> 6 51.0 (49,54] C- #> # … with 303 more rows17 / 31
- Here I show the
fct_recode(), manual work - what's other way to do this quickly
scores_schemes %>% ggplot(aes(x = range)) + geom_bar()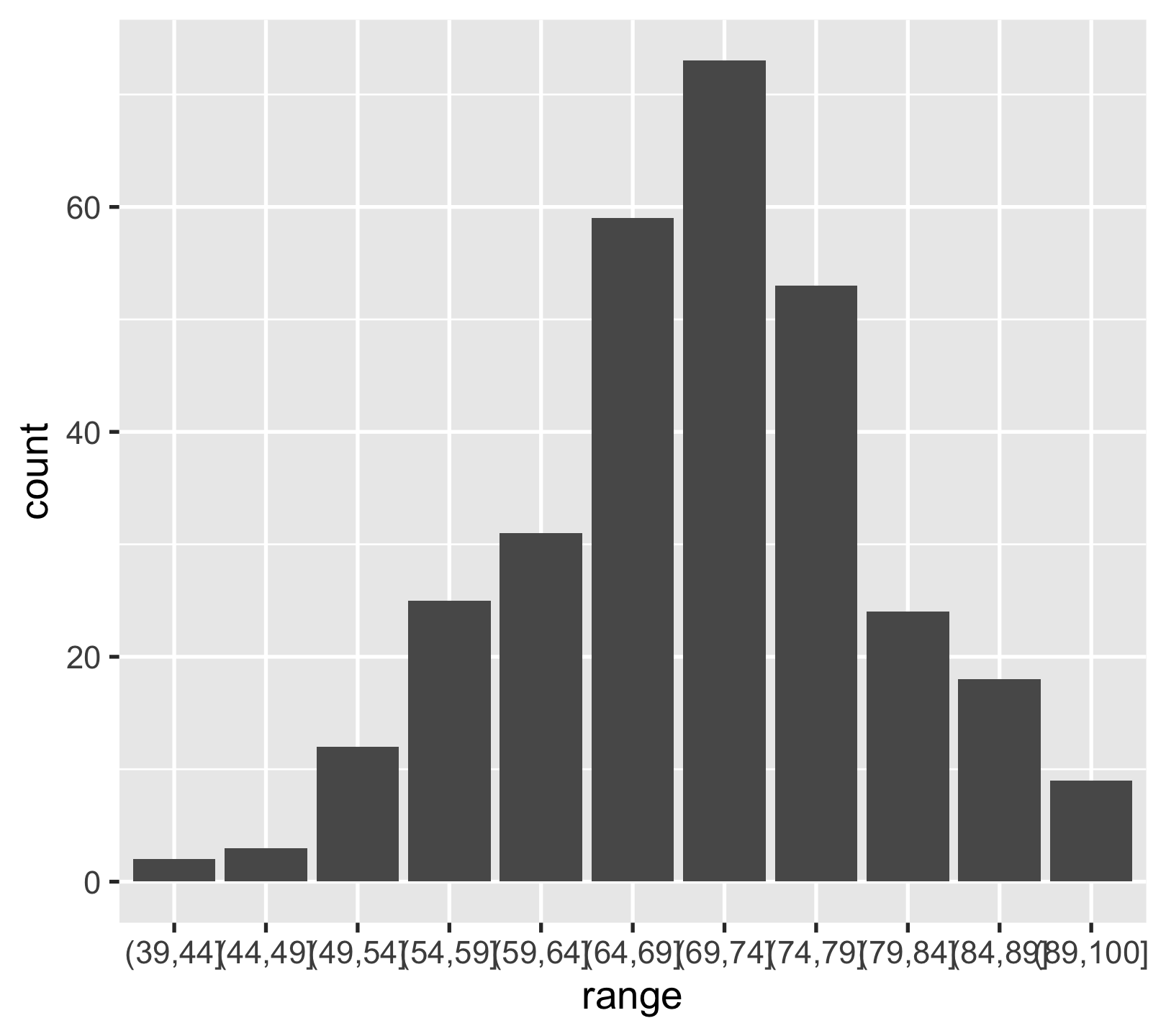
scores_schemes %>% ggplot(aes(x = grade)) + geom_bar()
18 / 31
Your turn
What function can we use to replace
fct_recode()for thescores_tbldata?
00:30
19 / 31
live demo: fct_rev()
⬇️ {lubridate} is NOT part of the core {tidyverse}, so load with
library(lubridate)Relative and exact time units:
- An instant is a specific moment in time, such as January 1st, 2012.
- An interval is a period of time that occurs between two specific instants.
- A duration records the time span in seconds, it will have an exact length since seconds always have the same length.
- A period records a time span in units larger than seconds, such as years, months, weeks, days, hours, and minutes.
20 / 31
- temporal data (recorded over time) is everywhere. Ur phone tracks your daily life.
- instant: timestamp
- leap seconds/years, time zones, DST
- lab04, tz
📆Dates
(td <- today())#> [1] "2021-03-31"class(td)#> [1] "Date"typeof(td)#> [1] "double"as.integer(td) # 1970-01-01#> [1] 18717⌚Date-times
(current <- now())#> [1] "2021-03-31 12:22:35 NZDT"class(current)#> [1] "POSIXct" "POSIXt"typeof(current)#> [1] "double"as.integer(current) # 1970-01-01 00:00:00#> [1] 161714655521 / 31
Create date-times
make_date(2021, c(3, 6), c(31, 4))#> [1] "2021-03-31" "2021-06-04"make_datetime(2021, c(3, 6), c(31, 4), c(16, 10))#> [1] "2021-03-31 16:00:00 UTC" "2021-06-04 10:00:00 UTC"make_datetime(2021, c(3, 6), c(31, 4), c(16, 10), tz = "Pacific/Auckland")#> [1] "2021-03-31 16:00:00 NZDT" "2021-06-04 10:00:00 NZST"22 / 31
Available time zones (~ 600‼️)
set.seed(220)OlsonNames()[sample(1:length(OlsonNames()), 32)]#> [1] "Pacific/Midway" "Africa/Asmera" #> [3] "Africa/Lusaka" "ROK" #> [5] "America/Montreal" "Europe/Dublin" #> [7] "Asia/Irkutsk" "Africa/Cairo" #> [9] "Asia/Dubai" "America/Yellowknife" #> [11] "Asia/Tbilisi" "America/Menominee" #> [13] "Atlantic/Azores" "GMT-0" #> [15] "America/Louisville" "Europe/Astrakhan" #> [17] "Pacific/Fakaofo" "America/Nome" #> [19] "Etc/GMT+10" "Pacific/Efate" #> [21] "GB-Eire" "Asia/Thimphu" #> [23] "US/Eastern" "Europe/Busingen" #> [25] "Australia/NSW" "America/Hermosillo" #> [27] "MET" "Pacific/Enderbury" #> [29] "America/Argentina/Rio_Gallegos" "Asia/Ashgabat" #> [31] "Africa/Dakar" "Canada/Atlantic"23 / 31
Parse date-times
ymd(c("2021/03/31", "2021-June-04"))#> [1] "2021-03-31" "2021-06-04"ymd_h(c("2021-03-31 16", "2021-June-04 10"))#> [1] "2021-03-31 16:00:00 UTC" "2021-06-04 10:00:00 UTC"(dttm <- ymd_h(c("2021-03-31 16", "2021-June-04 10"), tz = "Pacific/Auckland"))#> [1] "2021-03-31 16:00:00 NZDT" "2021-06-04 10:00:00 NZST"ymd(),ymd_h(),ymd_hm(),ymd_hms()dmy(),dmy_h(),dmy_hm(),dmy_hms()
mdy(),mdy_h(),mdy_hm(),mdy_hms()
24 / 31
Extract components of date-times
date(dttm)#> [1] "2021-03-31" "2021-06-04"year(dttm)#> [1] 2021 2021yday(dttm)#> [1] 90 155week(dttm)#> [1] 13 23day(dttm) # mday(dttm)#> [1] 31 4hour(dttm)#> [1] 16 10minute(dttm)#> [1] 0 0second(dttm)#> [1] 0 025 / 31
Extract months/weekdays of date-times
- month
month(dttm)#> [1] 3 6month(dttm, label = TRUE)#> [1] Mar Jun#> 12 Levels: Jan < Feb < Mar < ... < Dec- weekday
wday(dttm, week_start = 1)#> [1] 3 5wday(dttm, label = TRUE)#> [1] Wed Fri#> 7 Levels: Sun < Mon < Tue < ... < Satwday(dttm, label = TRUE, week_start = 1)#> [1] Wed Fri#> 7 Levels: Mon < Tue < Wed < ... < Sun26 / 31
Round, floor and ceiling date-times
floor_date(dttm, "3 hours")#> [1] "2021-03-31 15:00:00 NZDT" "2021-06-04 09:00:00 NZST"ceiling_date(dttm, "2 days")#> [1] "2021-04-02 NZDT" "2021-06-05 NZST"round_date(dttm, "1 month")#> [1] "2021-04-01 NZDT" "2021-06-01 NZST"27 / 31
Perform accurate math on date-times
dttm + 1#> [1] "2021-03-31 16:00:01 NZDT"#> [2] "2021-06-04 10:00:01 NZST"dttm + minutes(2)#> [1] "2021-03-31 16:02:00 NZDT"#> [2] "2021-06-04 10:02:00 NZST"dttm + hours(3)#> [1] "2021-03-31 19:00:00 NZDT"#> [2] "2021-06-04 13:00:00 NZST"dttm + days(4)#> [1] "2021-04-04 16:00:00 NZST"#> [2] "2021-06-08 10:00:00 NZST"dttm + weeks(5)#> [1] "2021-05-05 16:00:00 NZST"#> [2] "2021-07-09 10:00:00 NZST"dttm + months(6)#> [1] NA #> [2] "2021-12-04 10:00:00 NZDT"dttm + years(7)#> [1] "2028-03-31 16:00:00 NZDT"#> [2] "2028-06-04 10:00:00 NZST"28 / 31
Format date-times (also coerce to characters)
format(dttm)#> [1] "2021-03-31 16:00:00" "2021-06-04 10:00:00"format(dttm, "%Y/%b/%d")#> [1] "2021/Mar/31" "2021/Jun/04"format(dttm, "%y/%b/%d %H:%M:%S")#> [1] "21/Mar/31 16:00:00" "21/Jun/04 10:00:00"format(dttm, "on %d %B (%a)")#> [1] "on 31 March (Wed)" "on 04 June (Fri)"a/A: Abbreviated/full weekday name.b/B: Abbreviated or full month name.m: Month as decimal number (01-12 or 1-12).d: Day of the month as decimal number (01-31 or 0-31)w: Weekday as decimal number (0-6, Sunday is 0).y/Y: Year without/with century.- more on
?parse_date_time()
29 / 31
📽movies
movies$Release_Date[c(38:39, 268)]#> [1] "18-Oct-06" "1963-01-01" NAmovies %>% mutate( Release_Date = parse_date_time( Release_Date, c("%d-%b-%y", "%Y-%m-%d")), Year = year(Release_Date) ) %>% filter(Year < 2012) %>% ggplot(aes(Year, IMDB_Rating)) + geom_hex()
30 / 31


