STATS 220
Effective data visualisation👩🎨
1 / 43
Graphical perception 👀
2 / 43
Graphical perception 👀
1. Preattentive processing
2. Proximity
3. Position vs angle
4. Colour matters
2 / 43
- how human perceive a plot
- given the same amount of info from plots, which data type help us to perceive more accurate info
Preattentive processing
3 / 43
Preattentive processing

3 / 43
Preattentive processing


3 / 43
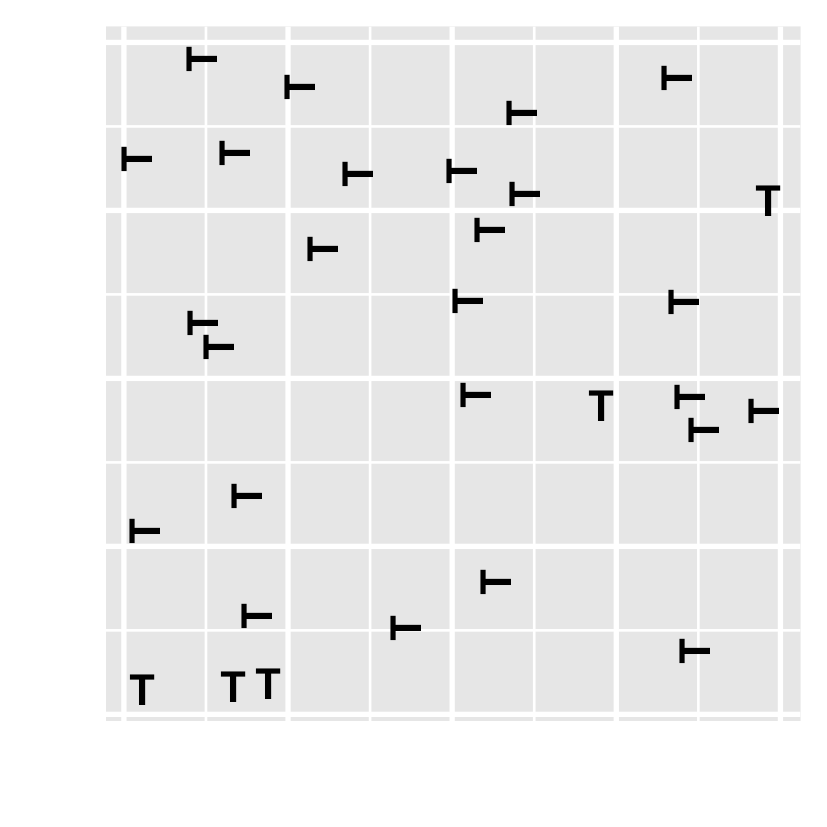
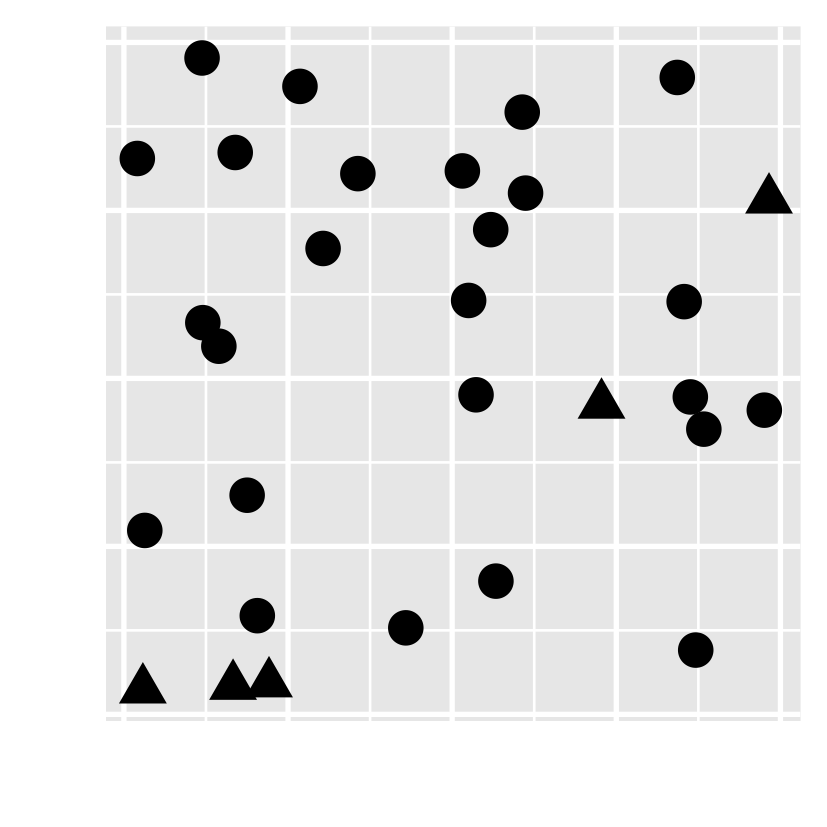
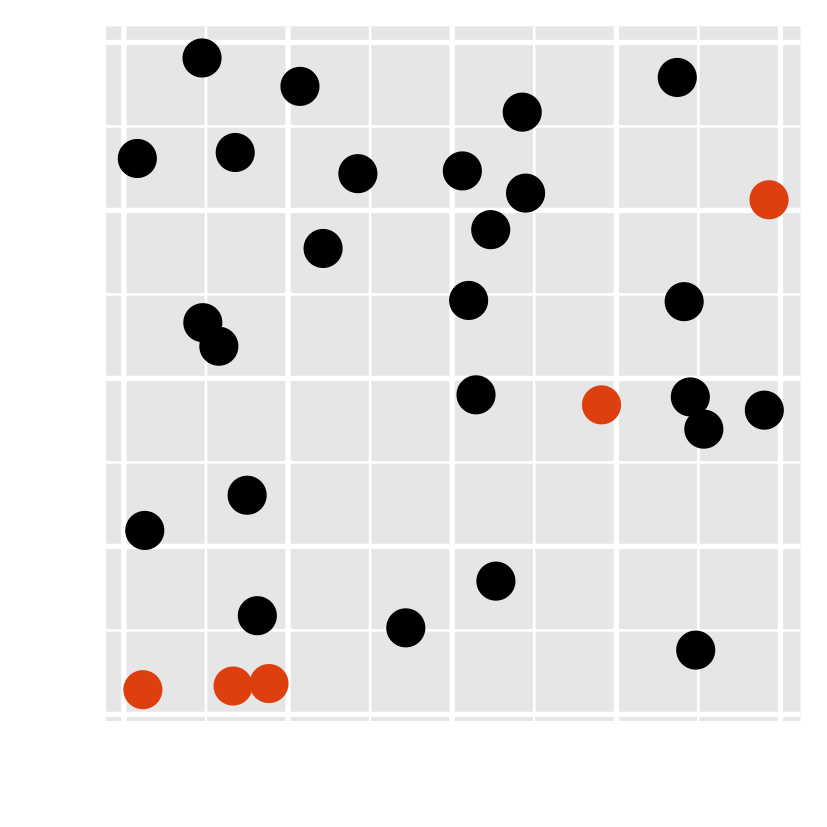
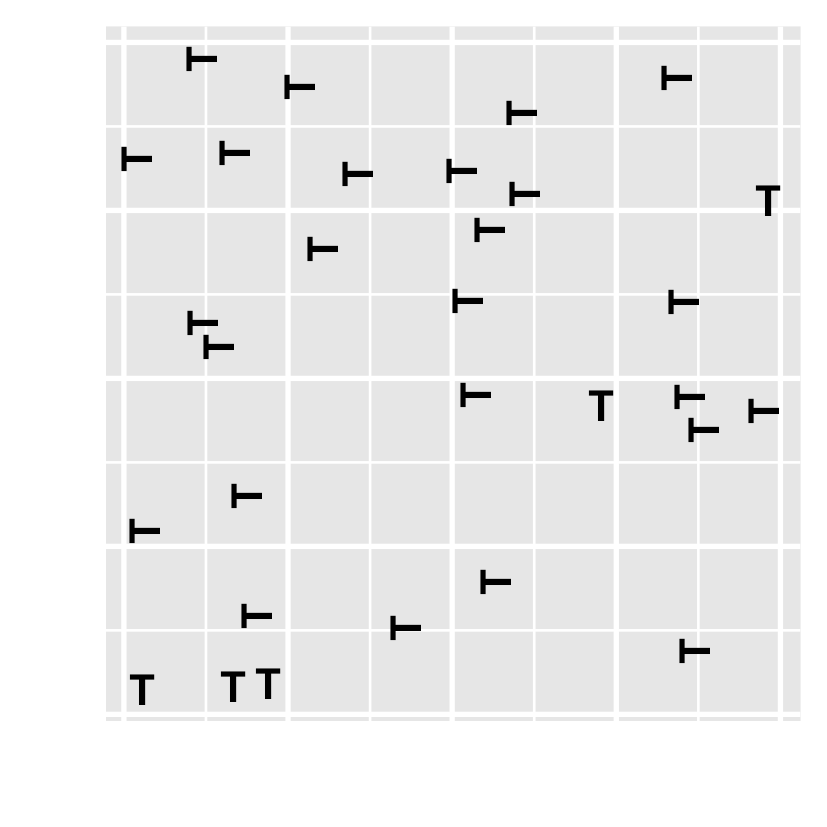
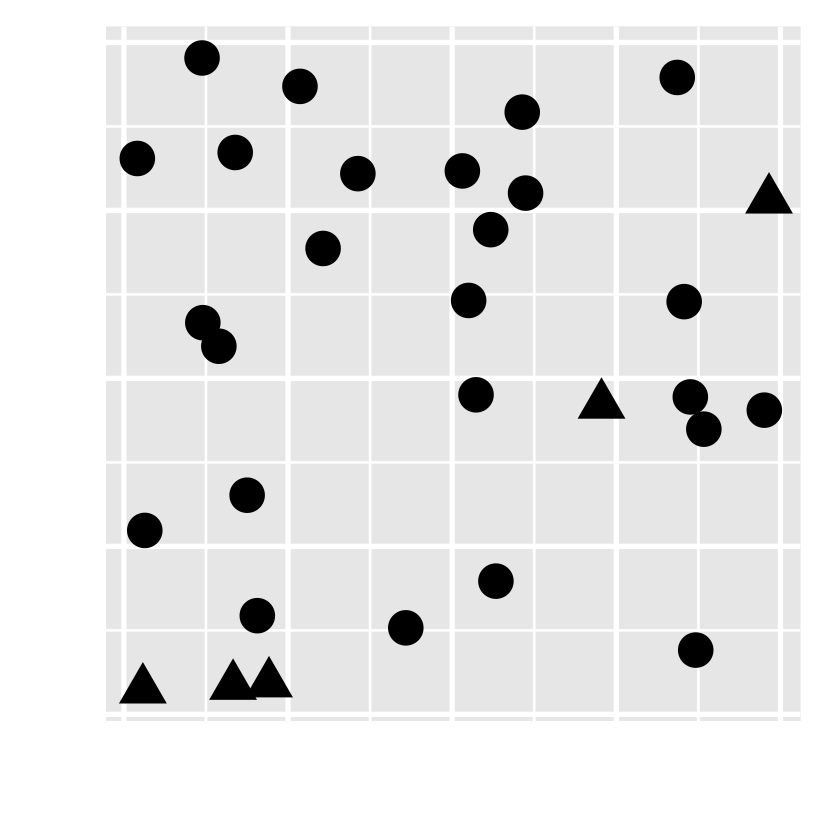
- Have you noticed there are unusual data points? Can you locate them?
- how about this one?
Preattentive processing colour > form (shape)
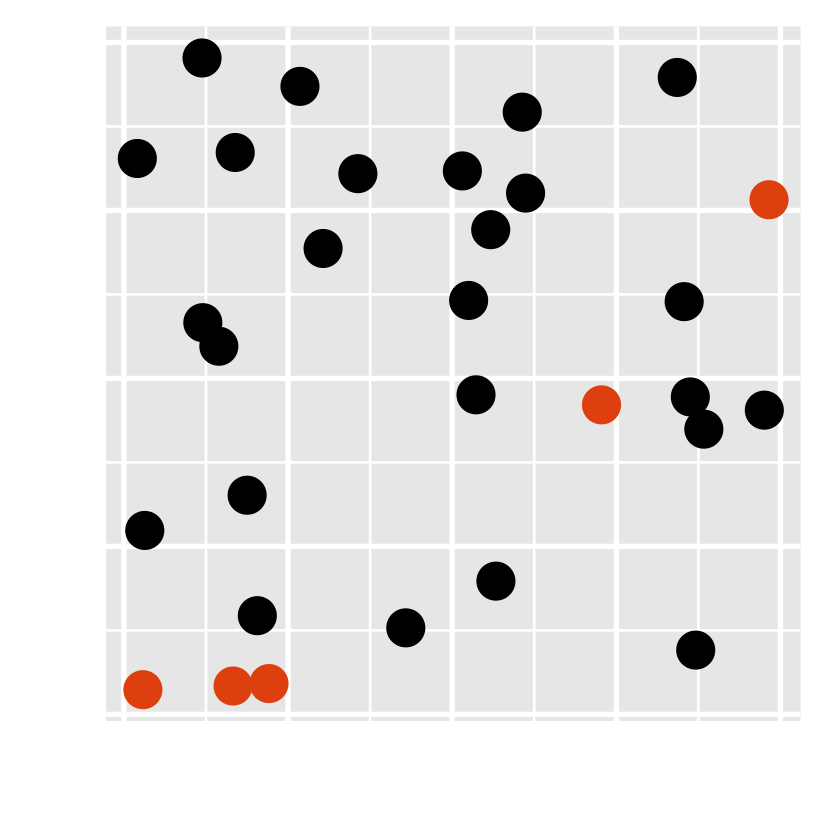
4 / 43
- Which plot helps you to distinguish the data points?
- Which plot consumes your least attention?
- viewers can sense certain features, b/f our mind starts to pay attention to any specific objs.
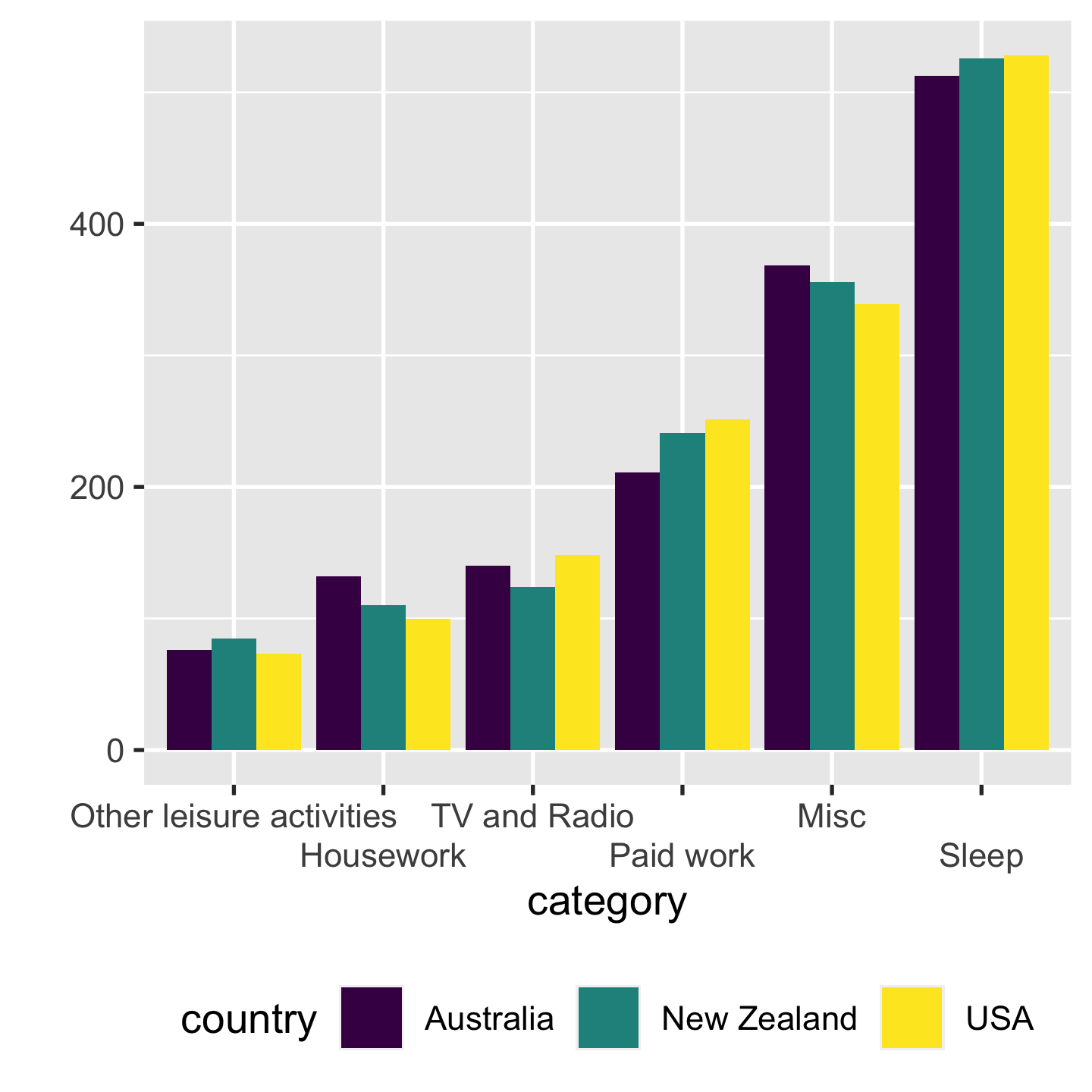
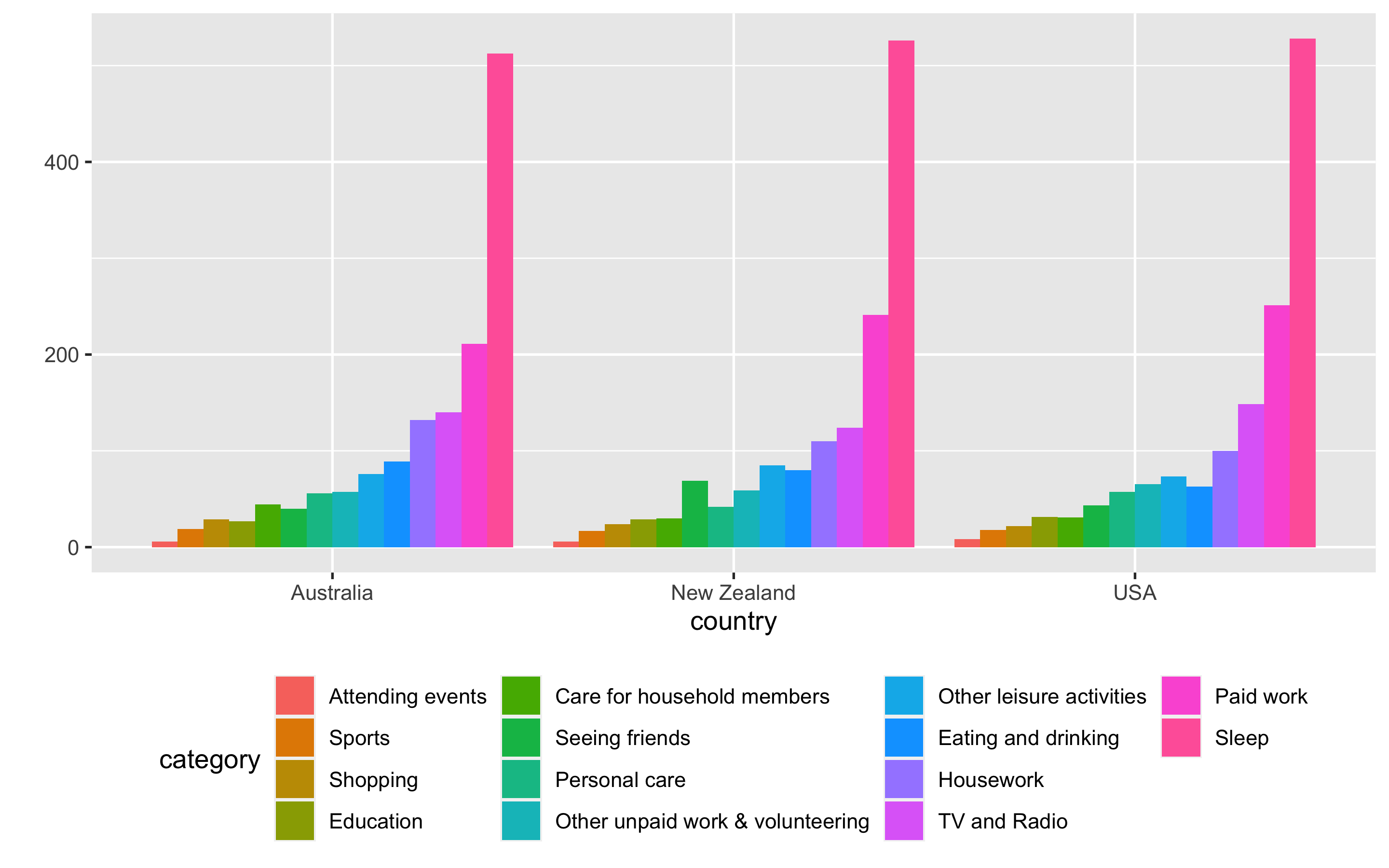
Proximity Make easy comparisons by grouping elements together
- compare time use by categories within each country
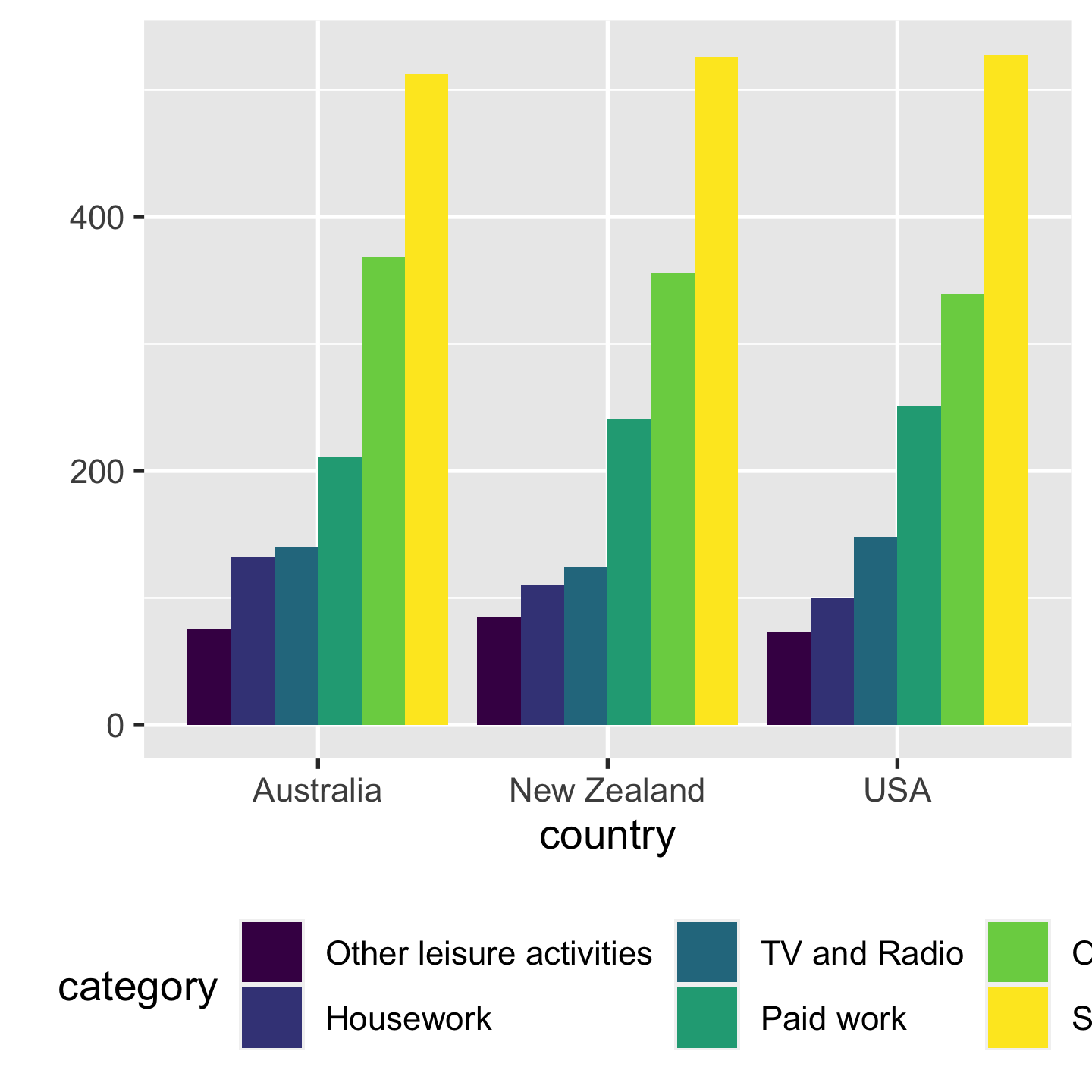
- compare time use by countries within each category
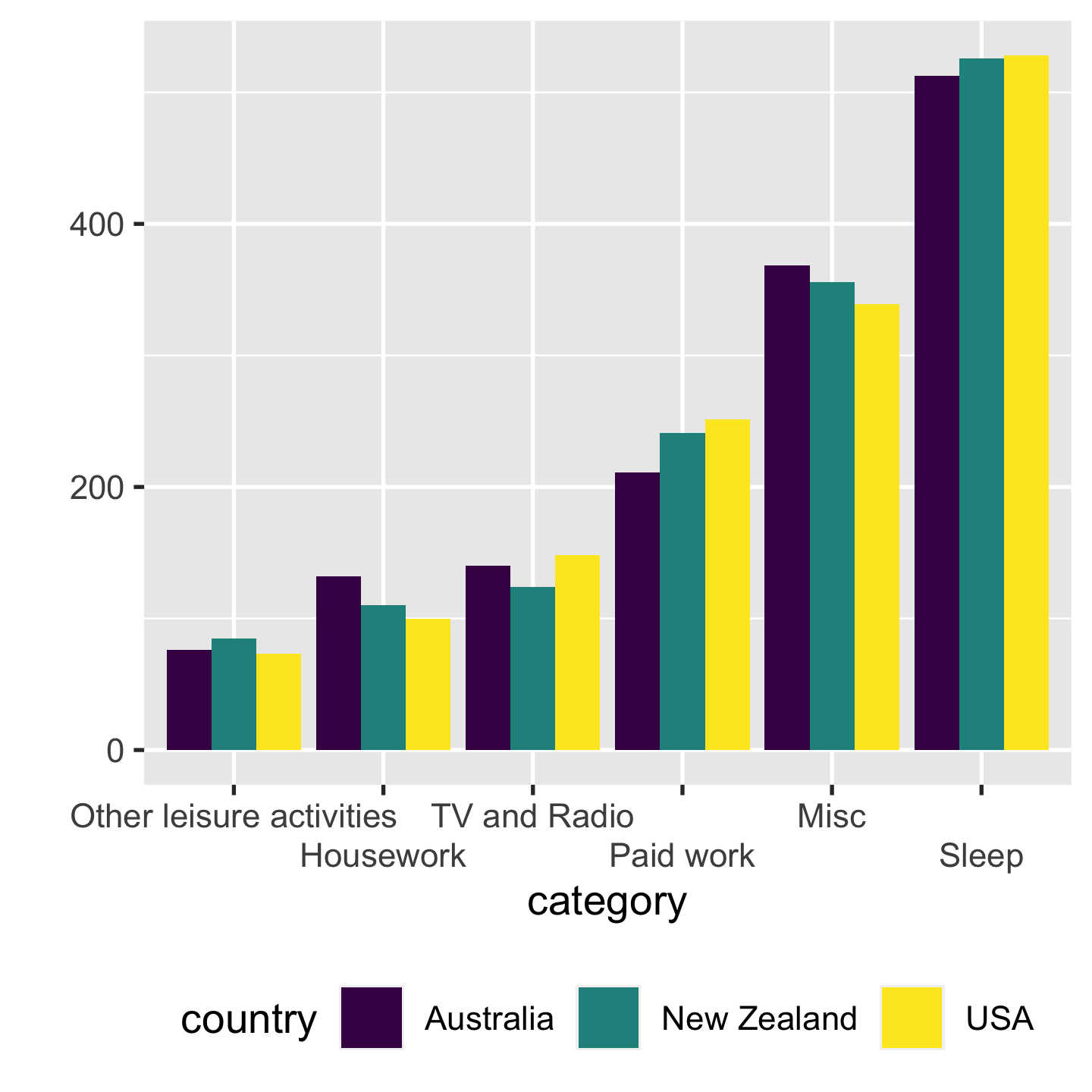
5 / 43
- left: it's not easy to compare how much time spent on sleep across countries
Position vs angle position > angle
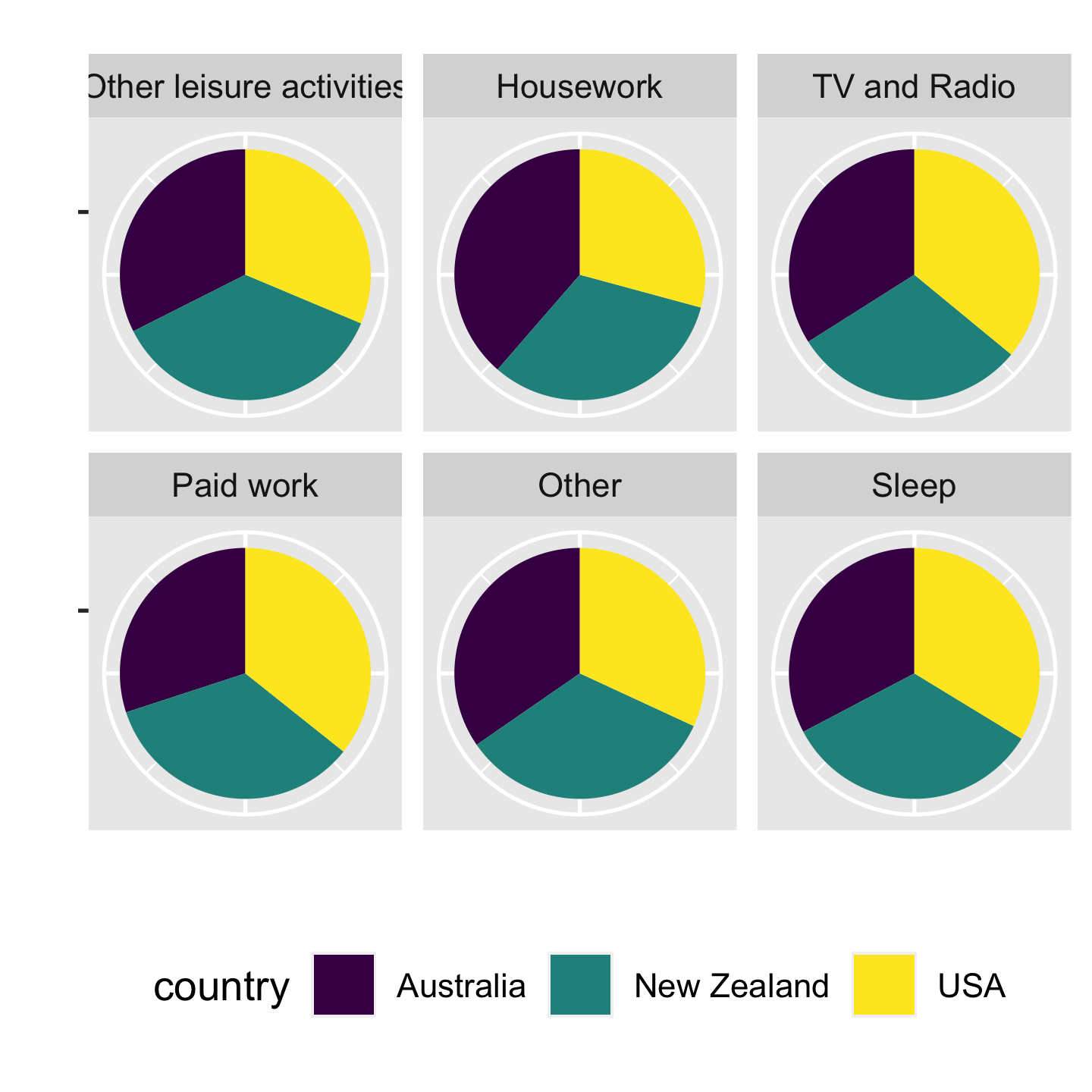 Pie charts are BAD‼️
Pie charts are BAD‼️
6 / 43
- "Other" and "Sleep", can u easily perceive these subtle differences from the pie charts?
- But
- A bar chart or dot chart is a preferable way of displaying this type of data.
Absolute vs relative positions absolute > relative
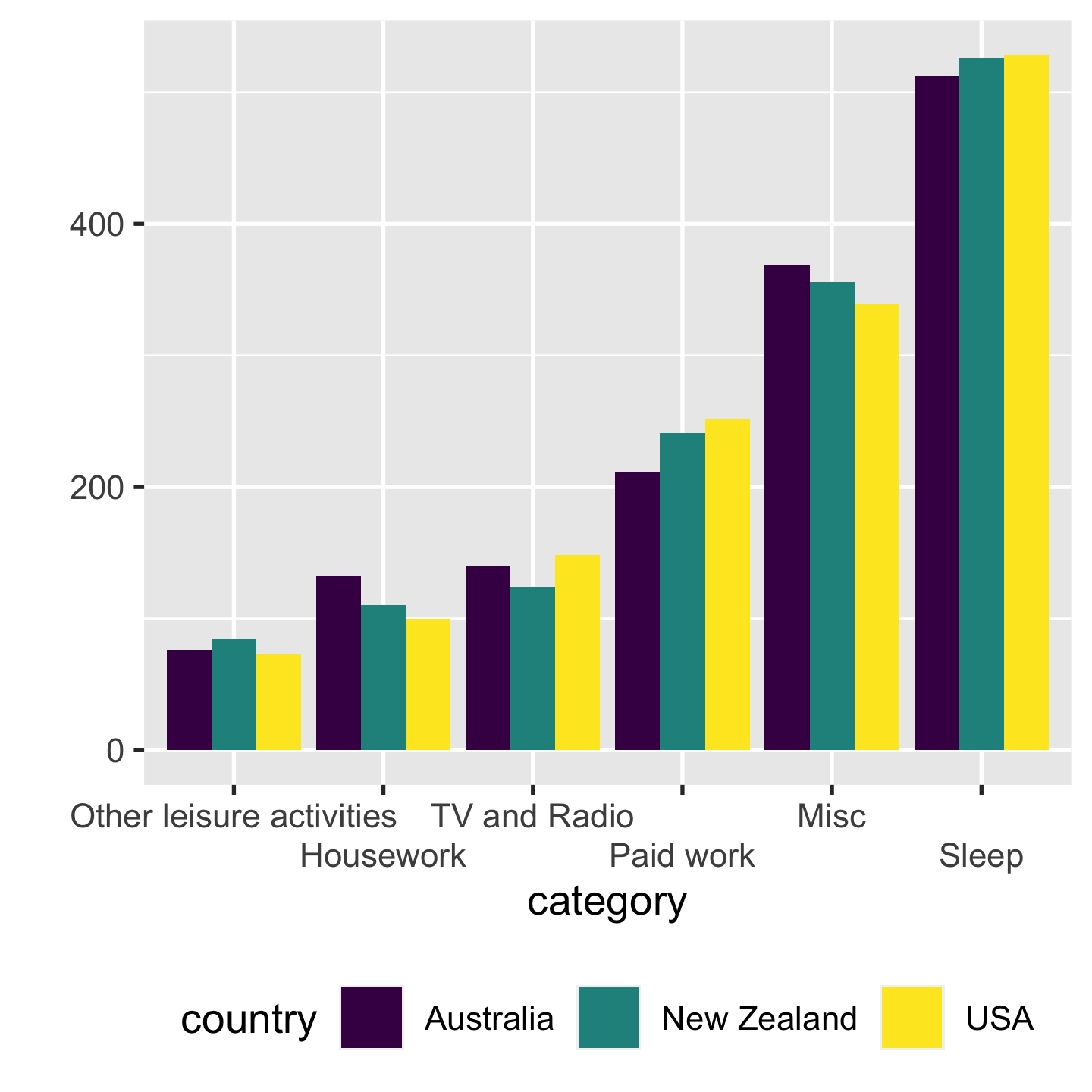
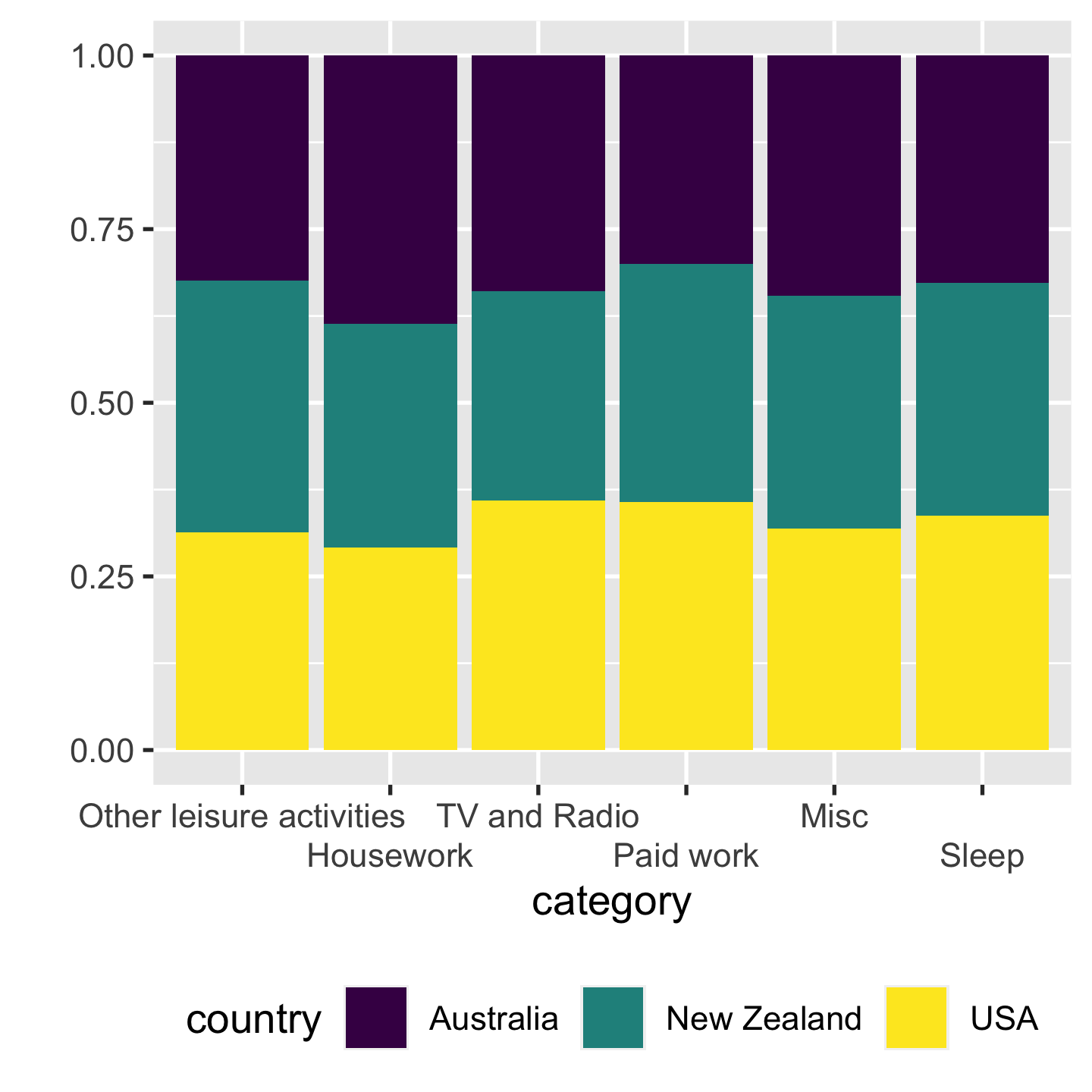
7 / 43
- absolute -> share the same base line. we compare their heights
- right: 100% bar chart. its much harder to compare NZ to others, bc NZ is rel.
- The eye is good at judging abs and bad at judging relative.
Colour matters
8 / 43
Colour matters
1. Colour spaces
2. Colour scales
3. Colour blindness
8 / 43
3 ways to represent colour spaces
- RGB
- HSV/HSL
- HCL for humans
9 / 43
RGB
- Red (0-255): amount of red light
- Green (0-255): amount of green light
- Blue (0-255): amount of blue light
image credit: Claus O. Wilke
10 / 43
- for computer & screen
HSV
- Hue (0-360): hue of the colour
- Saturation (0-1): colourfulness relative to the brightness of the colour
- Value (0-1): subjective perception of amount of light emitted
image credit: Claus O. Wilke
11 / 43
HSL
- Hue (0-360): hue of the colour
- Lightness (0-1): brightness relative to the brightness of a illuminated white
- Saturation (0-1): colourfulness relative to the brightness of the colour
image credit: Claus O. Wilke
12 / 43
HCL aka polar LUV
- Hue (0-360): hue of the colour
- Chroma (0-180): degree of vividness of a colour
- Luminance (0-100): amount of light emitted
image credit: Claus O. Wilke
13 / 43
HCL: perceptually-based and device-independent
Encoding too much
14 / 43
- default ggplot2 colour scales -> not colour blind friendly
- more than 7 qualitative colours, matching colours to categories are cumbersome
- colour can be effective tool to enhance
- choose colour wisely
Colour scales
3 fundamental use cases for colours in data visualisations:
- use colour to distinguish groups of data from each other
- use colour to represent data values
- use colour to highlight
3 types of colour palettes ColorBrewer
- Qualitative
- Sequential
- Diverging
15 / 43
Qualitative palettes for categorical data with no intrinsic ordering
colorspace::hcl_palettes("Qualitative", plot = TRUE, n = 7)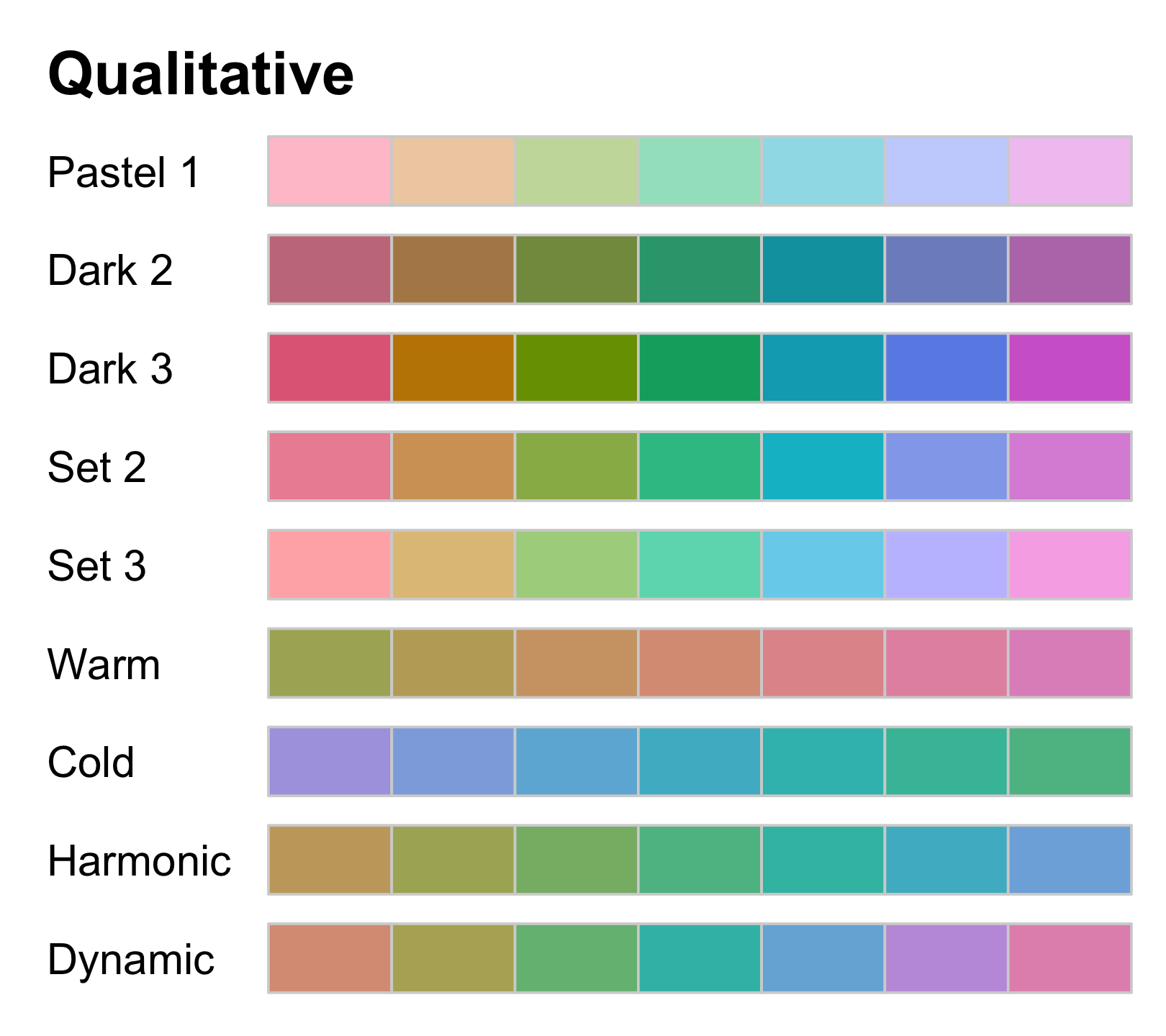
16 / 43
- use colour to distinguish discrete items/groups, but doesn't give impression of an order
- a finite set of specific colours that are chosen to look clearly distinct
- no one single colour stands out relative to the others
Sequential palettes for ordered data from high to low
colorspace::hcl_palettes("Sequential", plot = TRUE, n = 7)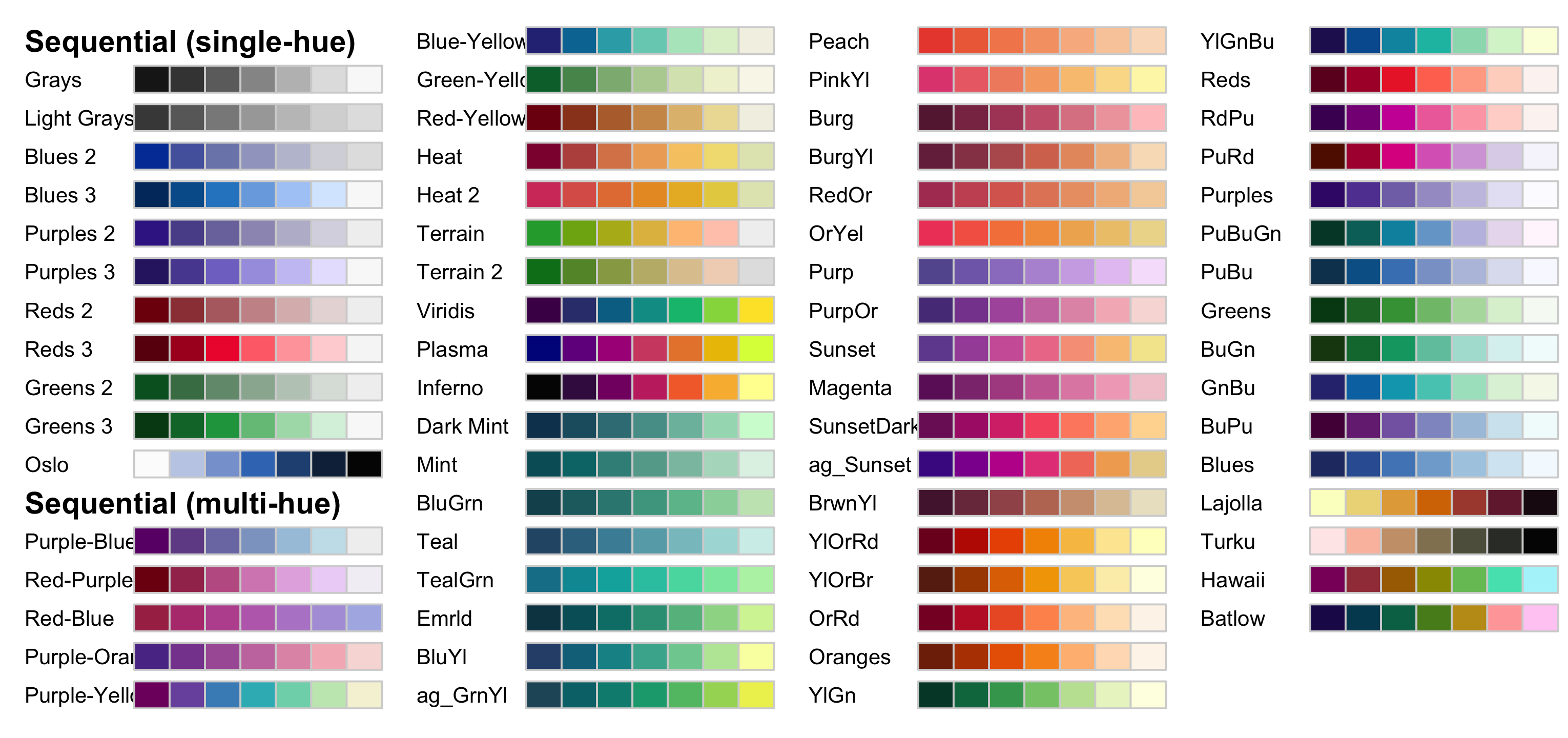
17 / 43
- heatmap: used colour to represent data values, like temperature
- representing continuous/ordered values
- colours indicate which data values are larger or smaller
- the diff bt colours shows the diff b/t data values
- seq colour needs to be perceived to vary uniformly across its entire range by changing hues
Diverging palettes for mid-range values and extremes at both ends
colorspace::hcl_palettes("Diverging", plot = TRUE, n = 7)
18 / 43
- vis the deviation of data values in one of 2 directions rel to a neutral midpoint
- a straightforward eg is vis +/- values
- think of a diverging scale as joining 2 seq sales at a common midpoint
Use colour palettes
time_use %>% ggplot(aes(country, time_minutes)) + geom_col( aes(fill = category), position = "dodge") + scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Dark2") + labs(y = "") + theme(legend.position = "bottom")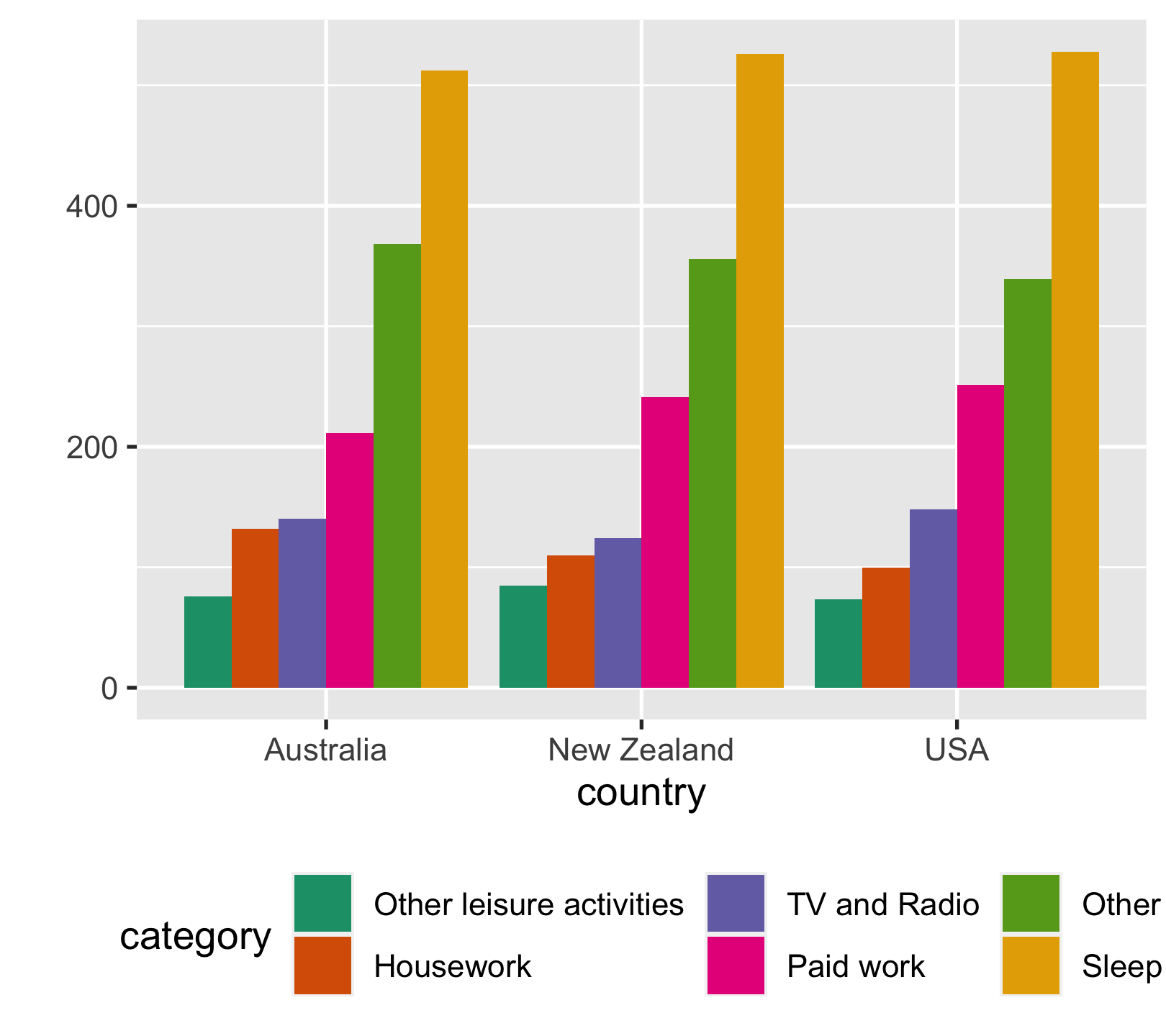
19 / 43
Set custom colours
time_use %>% ggplot(aes(country, time_minutes)) + geom_col( aes(fill = category), position = "dodge") + scale_fill_manual( values = c("#EF476F", "#FFD166", "#06D6A0", "#118AB2", "#073B4C", "grey")) + labs(y = "") + theme(legend.position = "bottom")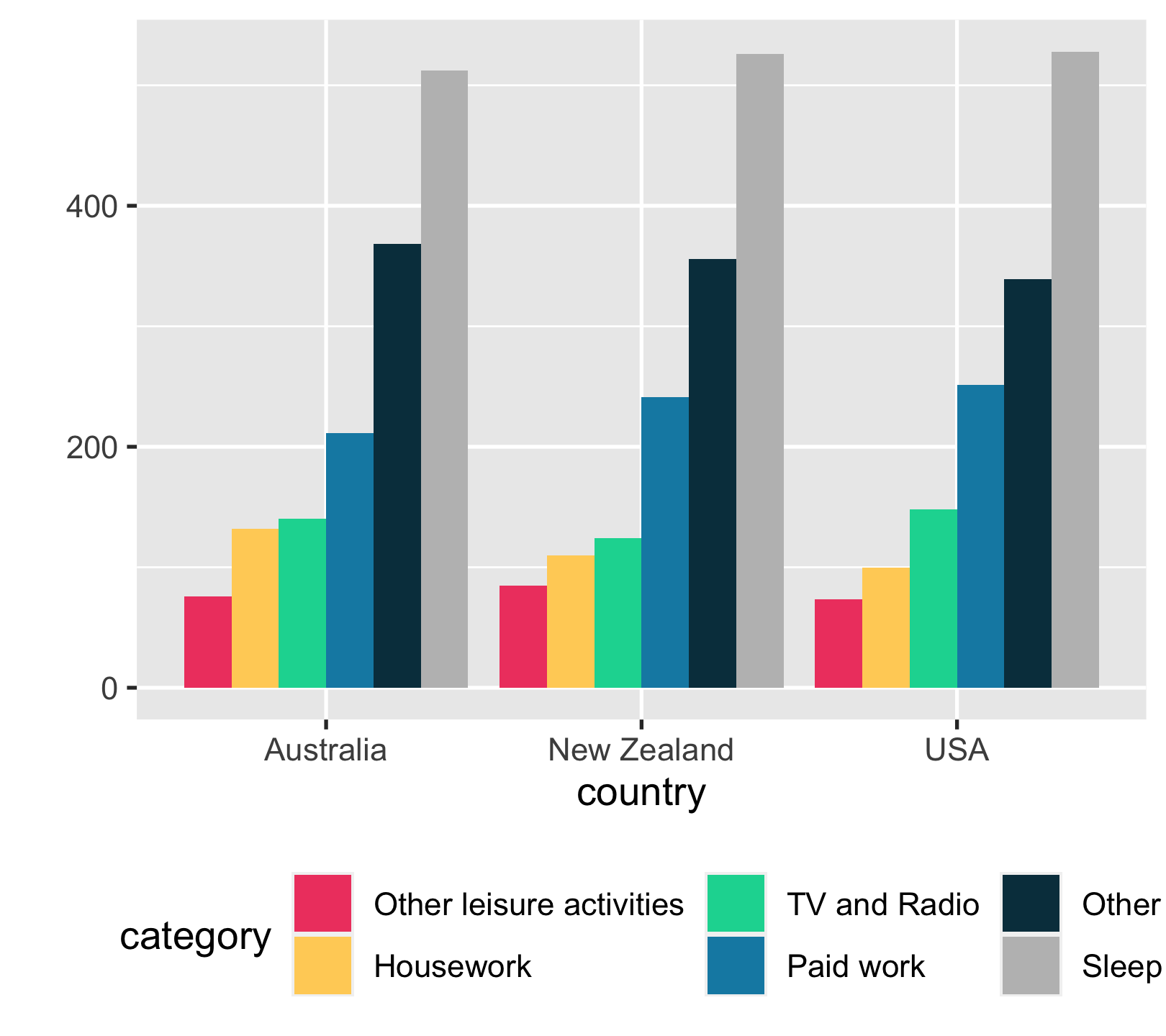
20 / 43
Colour-vision deficiency
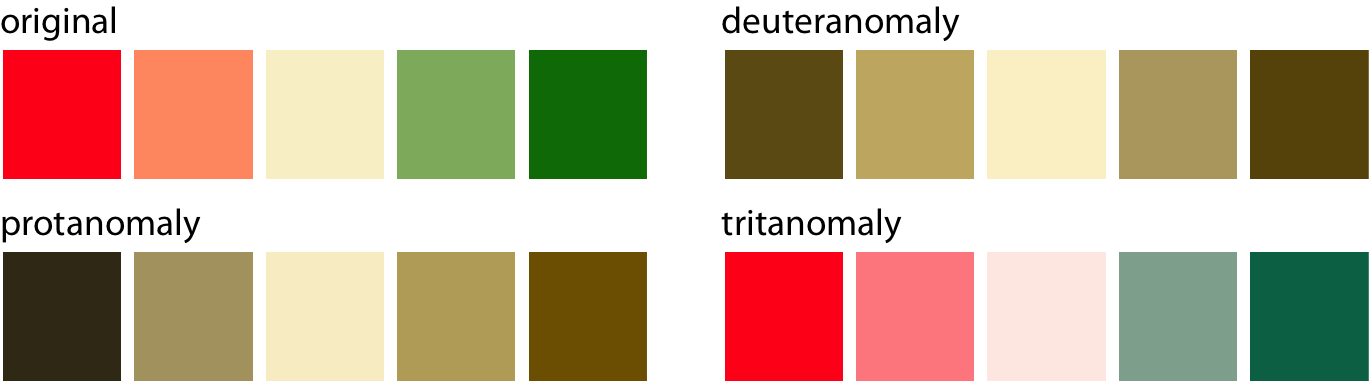
- Red-green colour-vision deficiency (deuteranomaly & protanomaly) is the most common.

- Blue-green colour-vision deficiency (tritanomaly) is rare but does occur.
ℹ️ Approximately 8% of males and 0.5% of females suffer from some sort of color-vision deficiency.
reference: Claus O. Wilke Fundamentals of Data Visualization
21 / 43
- A small prop of people with impaired colour vision have difficulty to distinguish certain types of colours
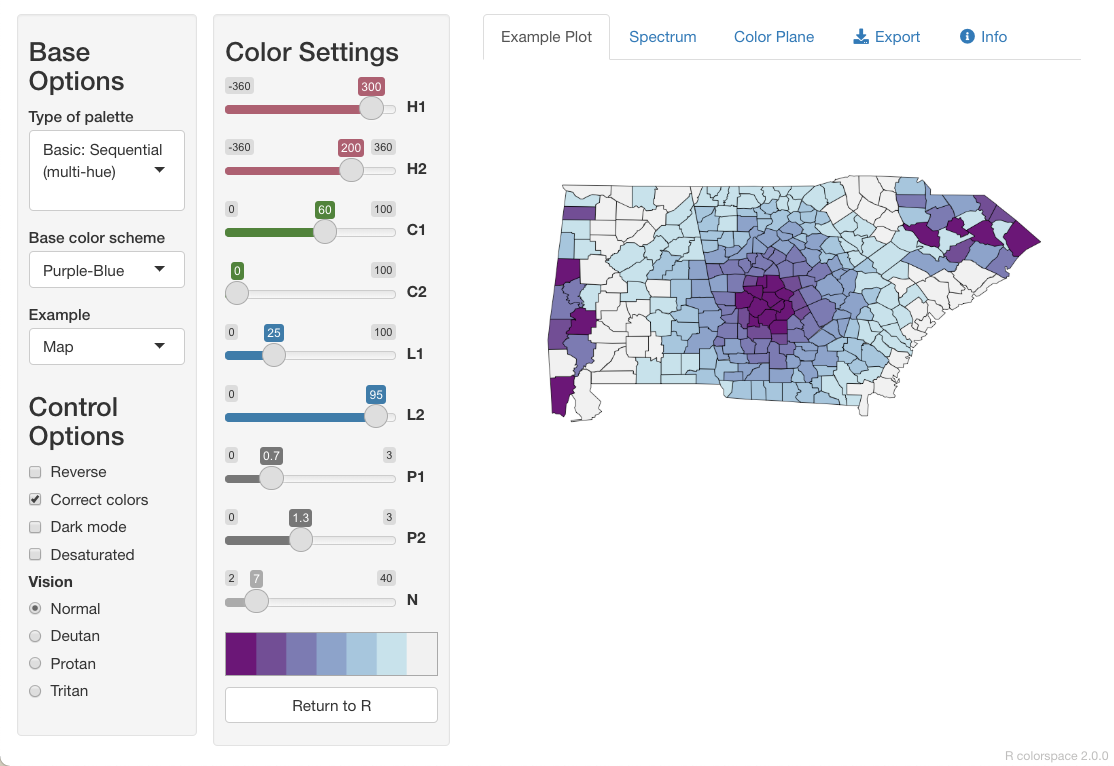
Choose colours using {colorspace}
colorspace::hclwizard()
colorspace::hcl_color_picker()
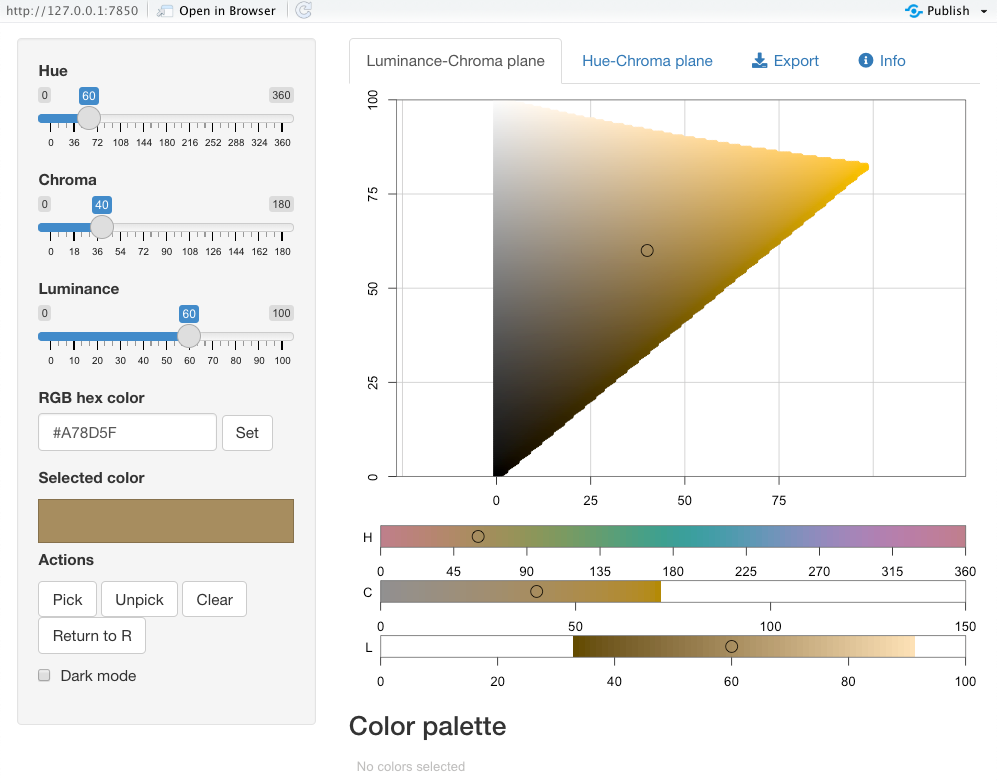
22 / 43
Scales
- Control how data is mapped to perceptual properties, and produce guides (axes and legends) which allow us to read the plot.
- Important arguments:
breaks,labels, andlimits. - Naming scheme:
scale_[aes]_[datatype]()
23 / 43
| scale | Description |
|---|---|
| scale_alpha, scale_alpha_continuous, scale_alpha_binned, scale_alpha_discrete | Alpha transparency scales |
| scale_x_binned, scale_y_binned | Positional scales for binning continuous data (x & y) |
| scale_colour_brewer, scale_fill_brewer, scale_colour_distiller, scale_fill_distiller | Sequential, diverging and qualitative colour scales from colorbrewer.org |
| scale_colour_continuous, scale_fill_continuous, scale_colour_binned, scale_fill_binned | Continuous and binned colour scales |
| scale_colour_discrete, scale_fill_discrete | Discrete colour scales |
24 / 43
Publication-ready visualisation 👩🎨
25 / 43
Towards publication-ready visualisation
#MakingOf of last week's #TidyTuesday plot https://t.co/Jsg41id5Nw pic.twitter.com/dP6tSrjHy0
— Georgios Karamanis (@geokaramanis) March 22, 2021
26 / 43
Exploratory data visualisation
- For internal use only. Need to be able to create rapidly because your first attempt will never be the most revealing.
- Iteration is crucial for developing multiple displays of your data.
Communication graphics
- When you communicate your findings, you need to spend much time polishing your graphics to eliminate distractions and focus on the storytelling.
- Iteration is crucial to ensure all the bits and pieces works well: labels, color choices, tick marks...
27 / 43
Case study: COVID-19
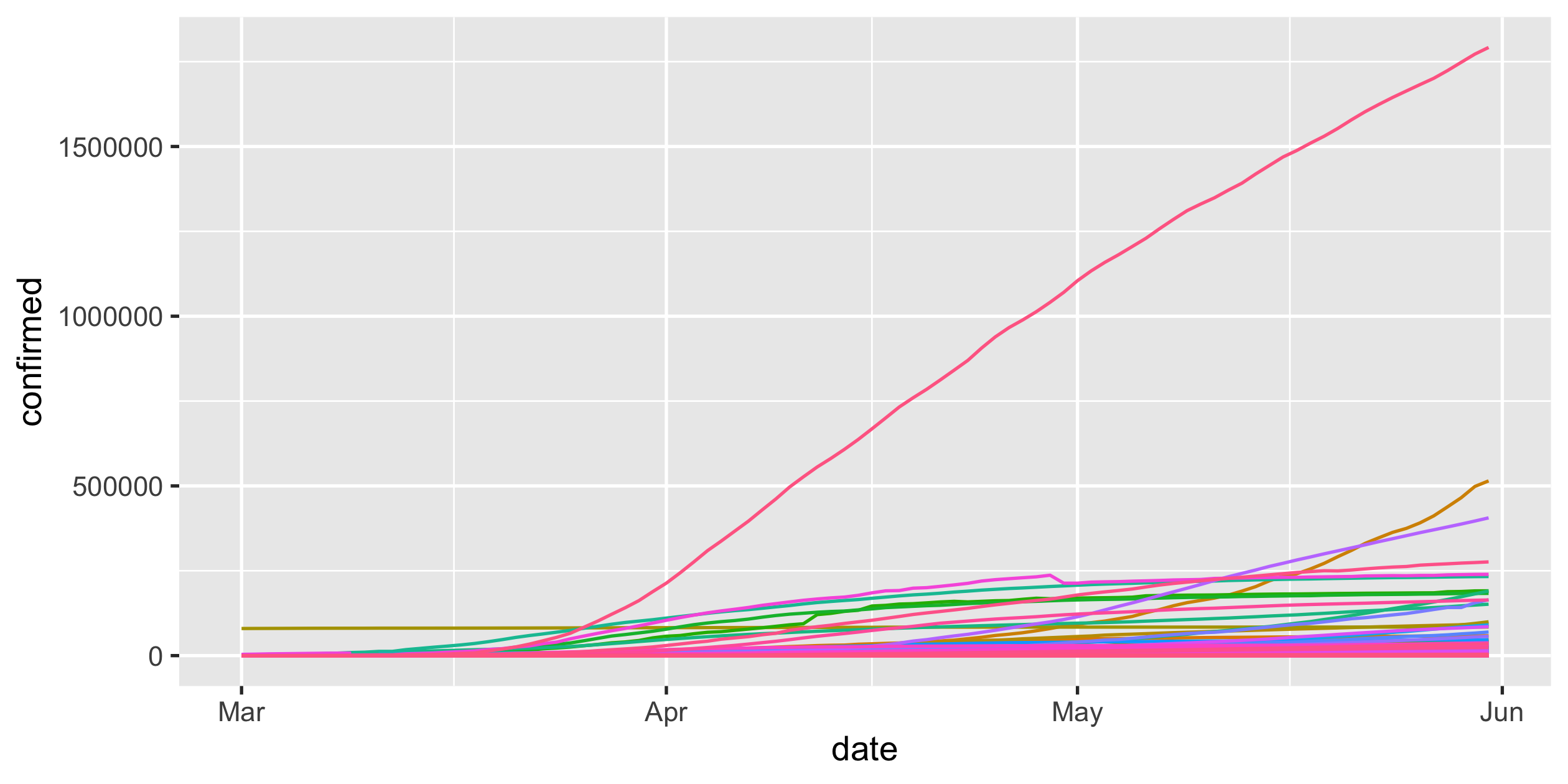
covid19 <- read_csv("data/covid19-daily-cases.csv")covid19#> # A tibble: 15,677 x 3#> country_region date confirmed#> <chr> <date> <dbl>#> 1 Afghanistan 2020-03-01 1#> 2 Afghanistan 2020-03-02 1#> 3 Afghanistan 2020-03-03 2#> 4 Afghanistan 2020-03-04 4#> 5 Afghanistan 2020-03-05 4#> 6 Afghanistan 2020-03-06 4#> # … with 15,671 more rows28 / 43
full screen of legends
perceive the rate of infections, slowing down
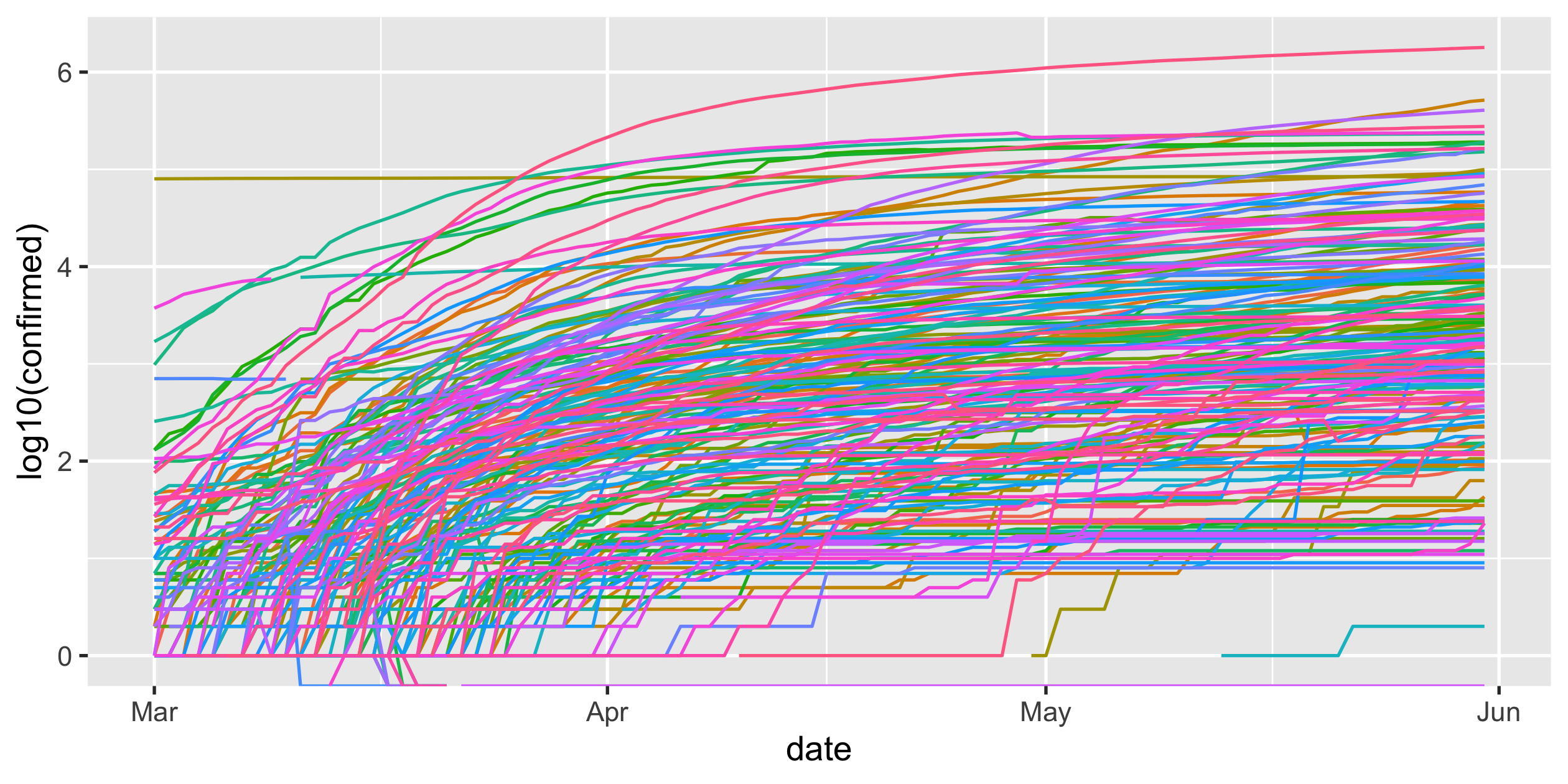
COVID-19
- scale-y
Logarithmic scale
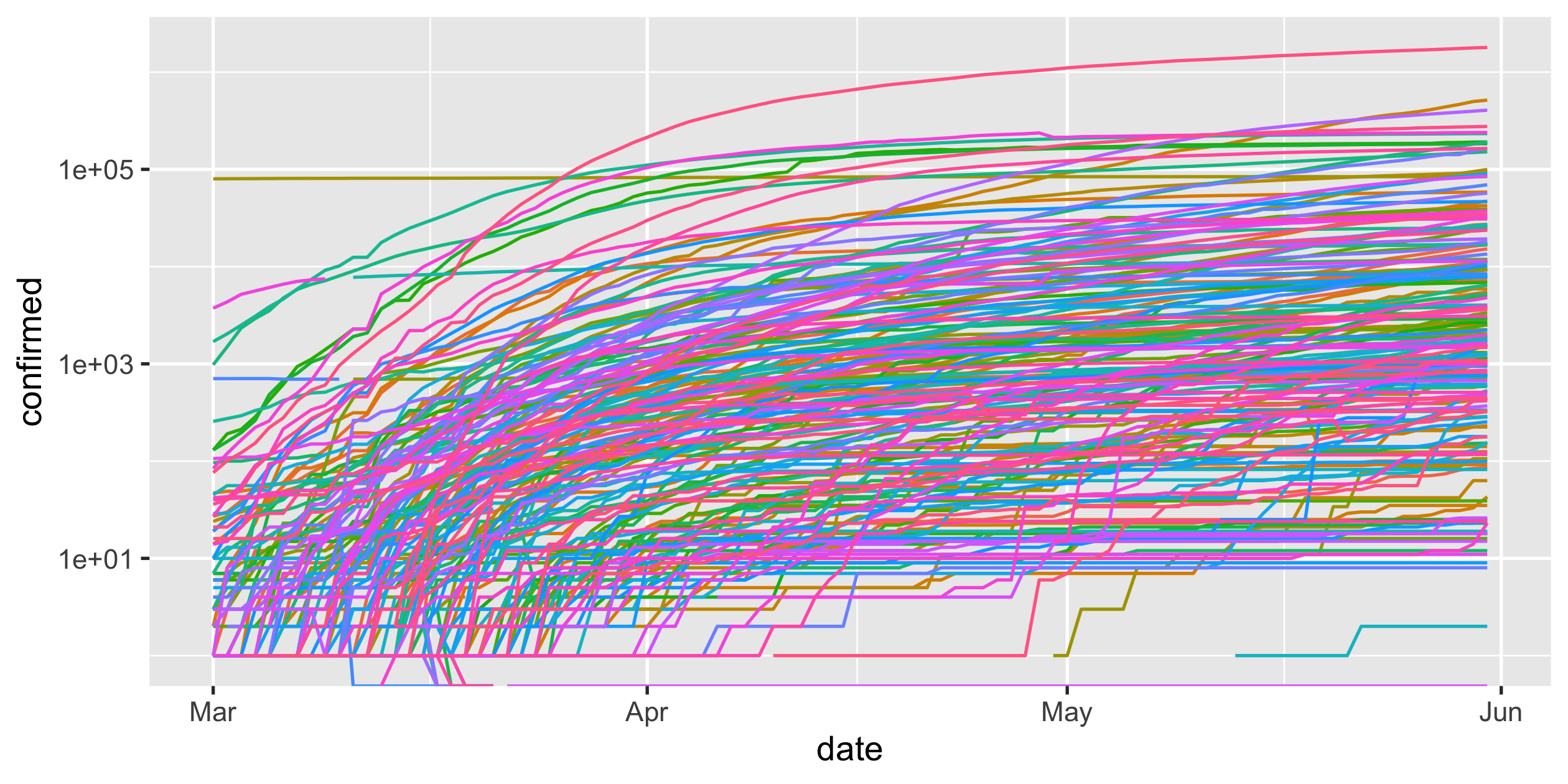
covid19 %>% ggplot(aes( x = date, y = confirmed, colour = country_region)) + geom_line() + guides(colour = FALSE) + scale_y_log10()Rob J Hyndman's blog post on Why log ratios are useful for tracking COVID-19
31 / 43
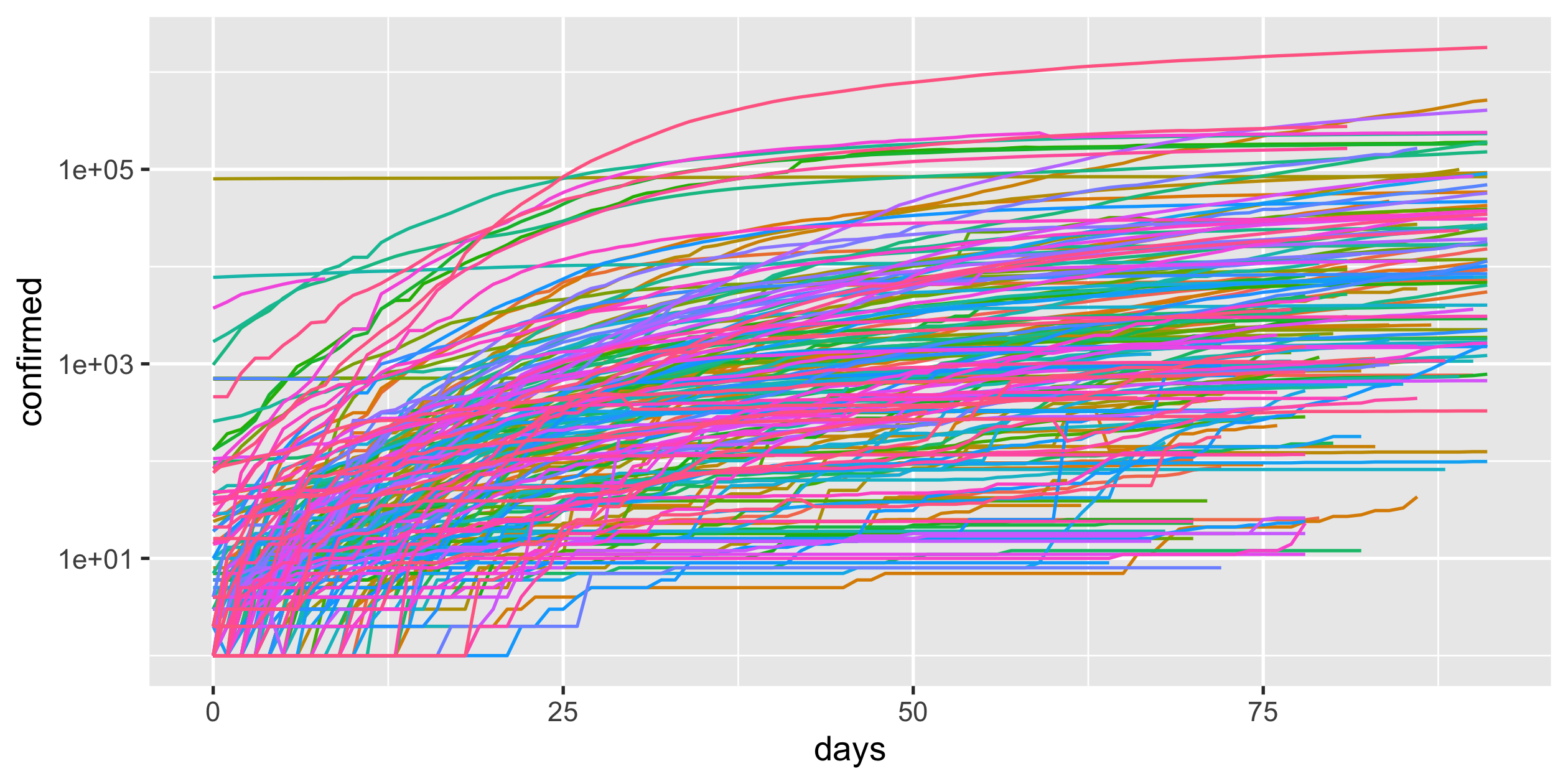
COVID-19
- scale-y
- scale-x
covid19_rel <- covid19 %>% group_by(country_region) %>% mutate(days = as.numeric(date - min(date))) %>% ungroup()covid19_rel#> # A tibble: 15,677 x 4#> country_region date confirmed days#> <chr> <date> <dbl> <dbl>#> 1 Afghanistan 2020-03-01 1 0#> 2 Afghanistan 2020-03-02 1 1#> 3 Afghanistan 2020-03-03 2 2#> 4 Afghanistan 2020-03-04 4 3#> 5 Afghanistan 2020-03-05 4 4#> 6 Afghanistan 2020-03-06 4 5#> # … with 15,671 more rows32 / 43
log(0) -> Inf
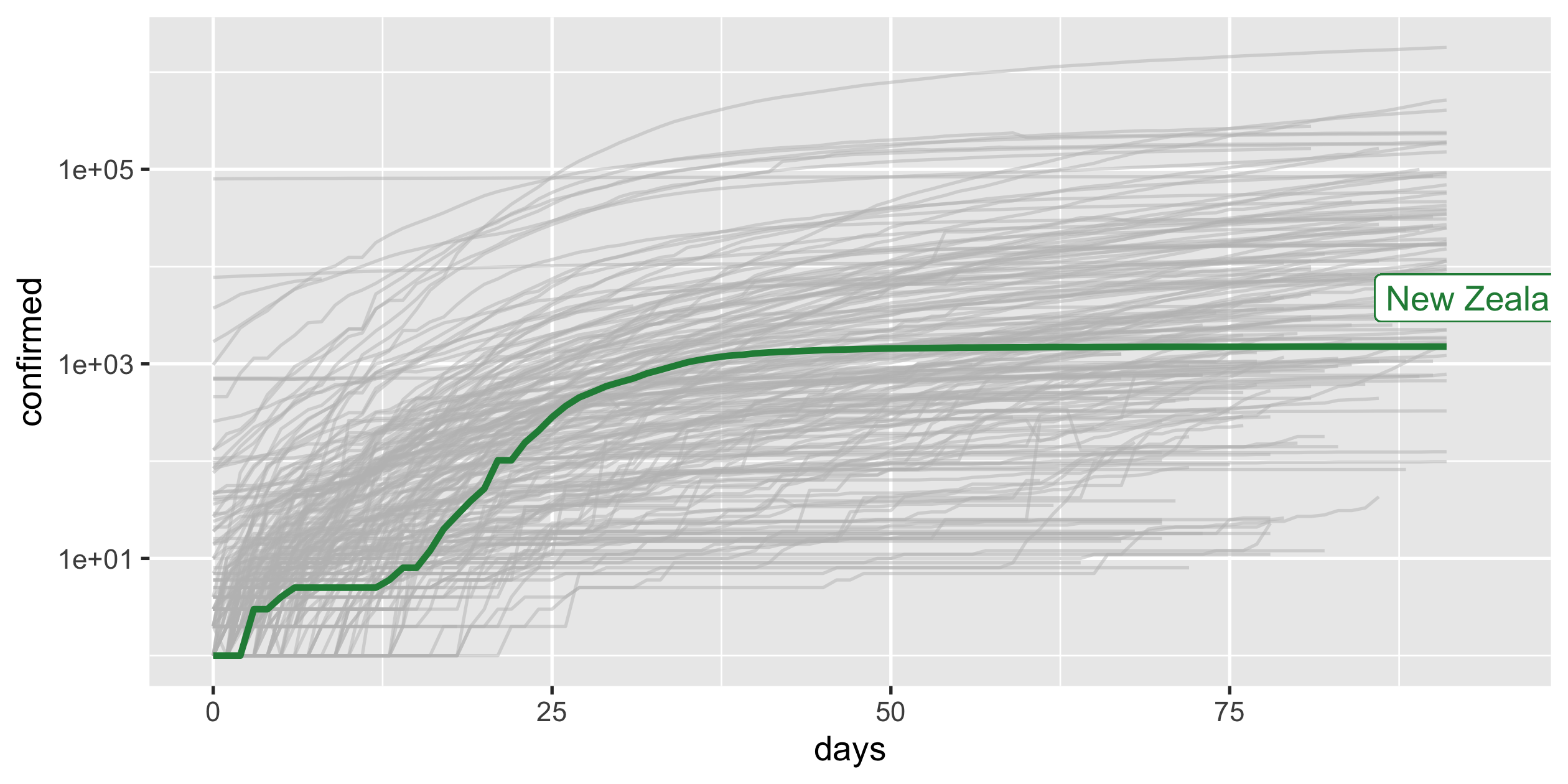
COVID-19
- scale-y
- scale-x
- highlight
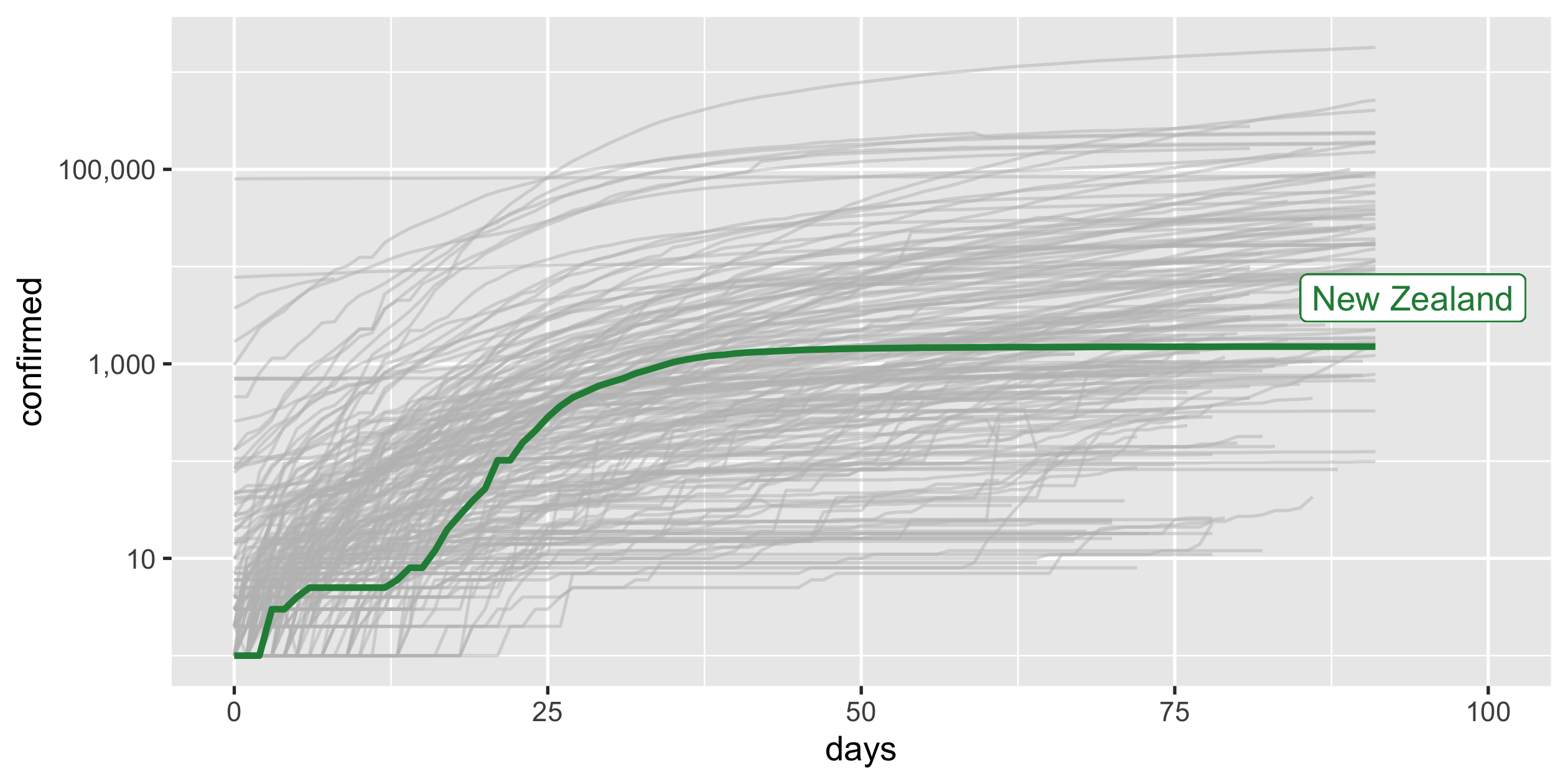
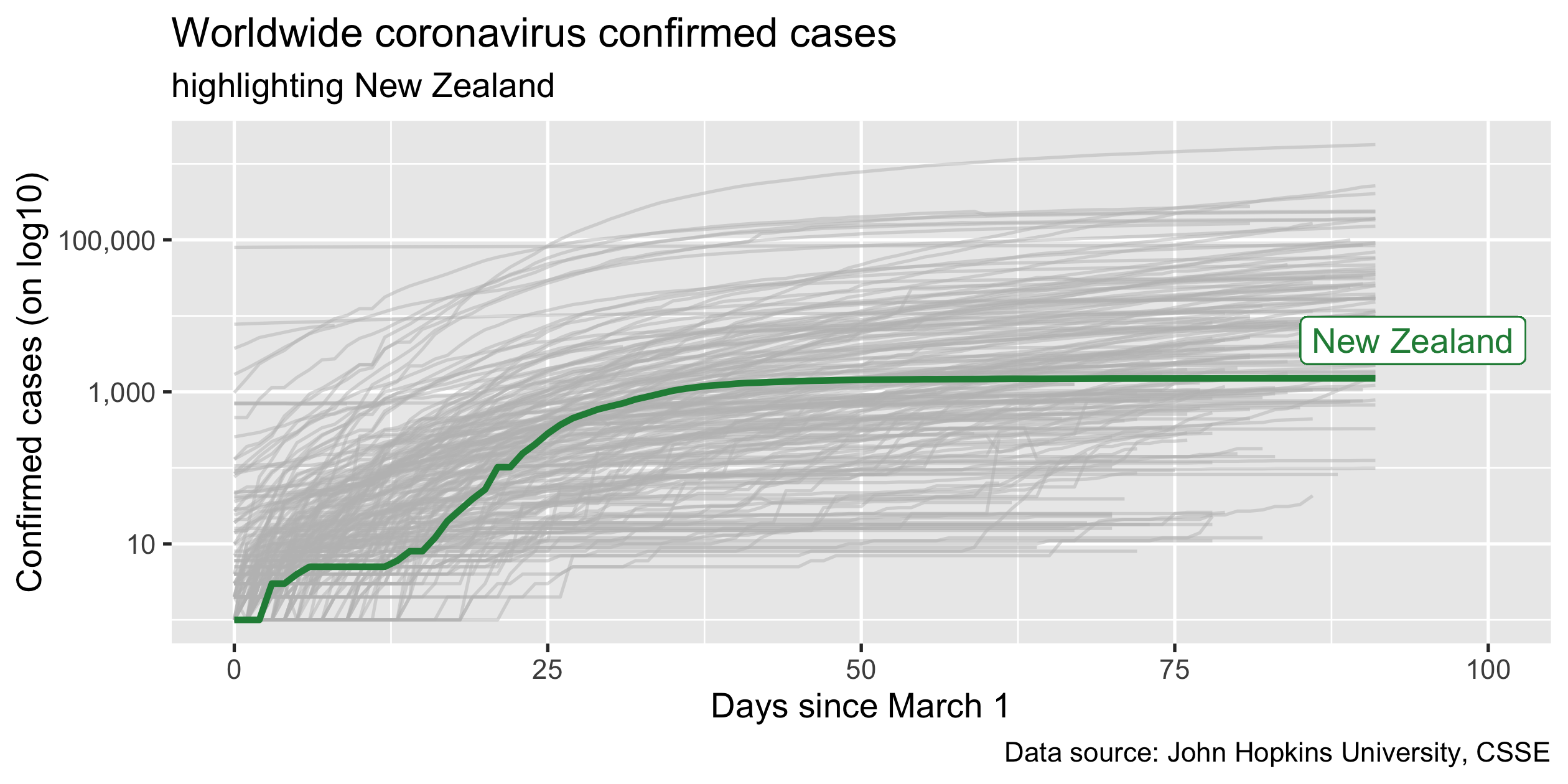
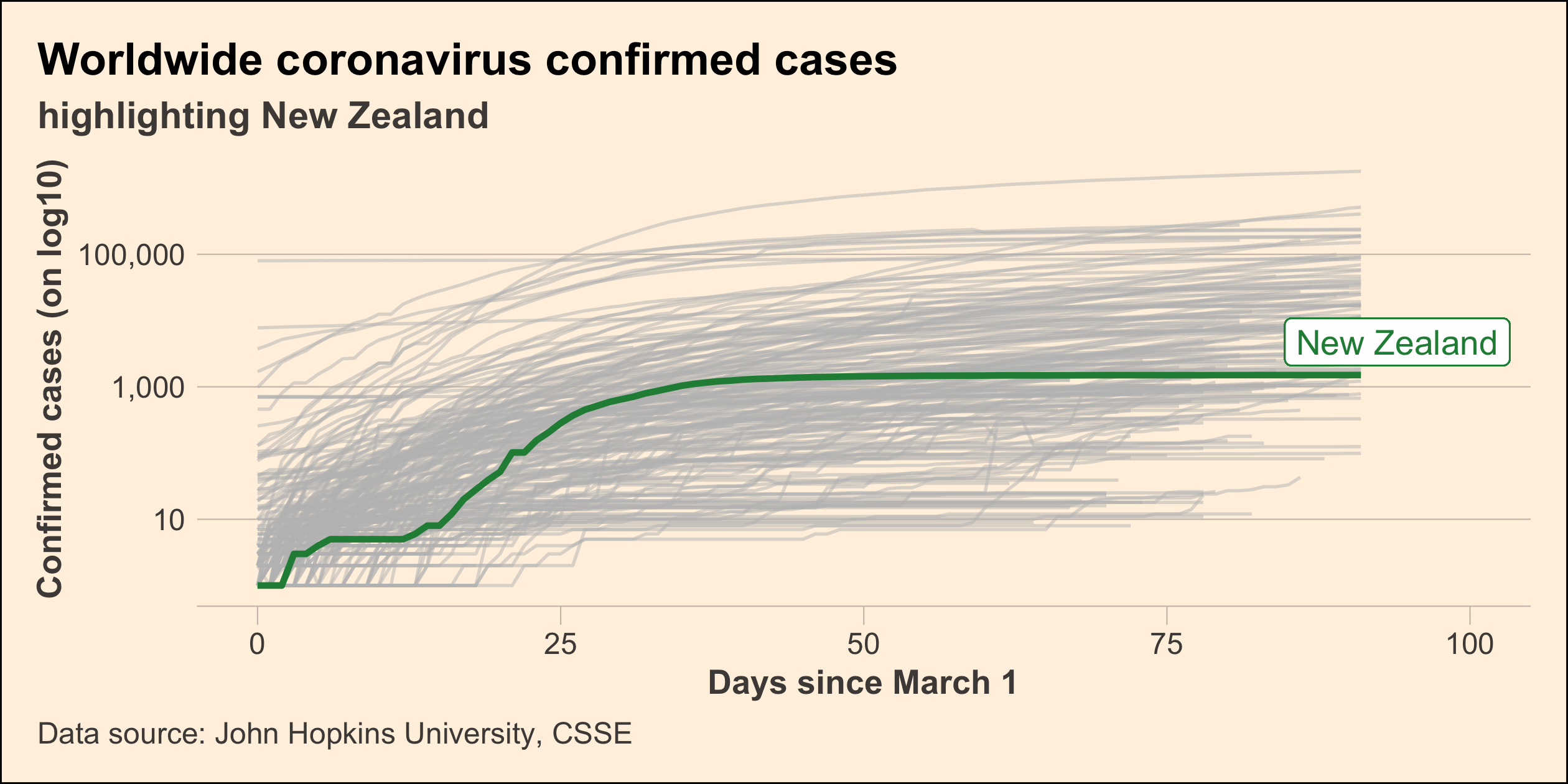
Highlight New Zealand
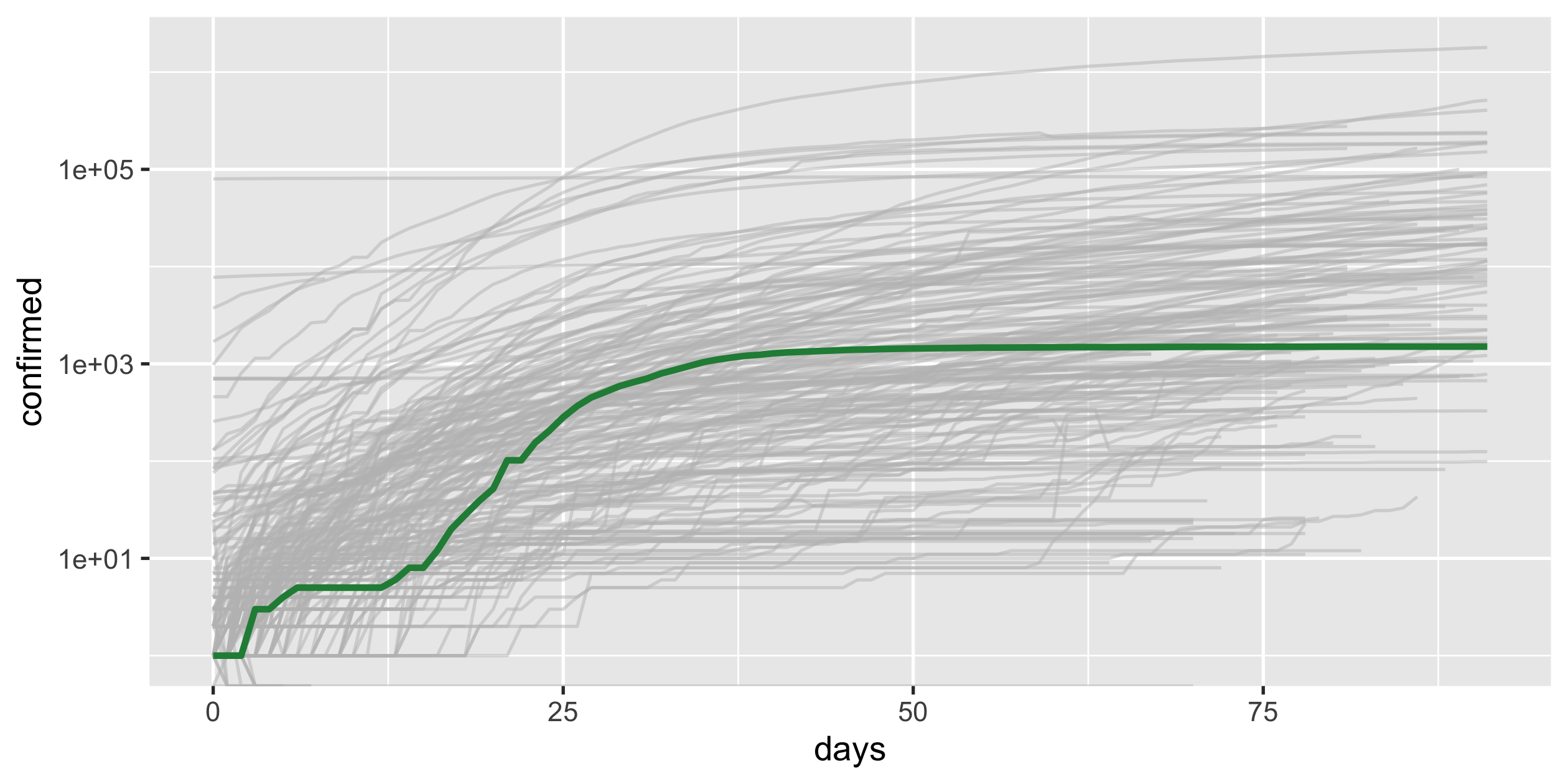
covid19_nz <- covid19_rel %>% filter(country_region == "New Zealand")p_nz <- covid19_rel %>% ggplot(aes(x = days, y = confirmed, group = country_region)) + geom_line(colour = "grey", alpha = 0.5) + geom_line(colour = "#238b45", size = 1, data = covid19_nz) + scale_y_log10() + guides(colour = FALSE)p_nz34 / 43
COVID-19
- scale-y
- scale-x
- highlight
- annotate
- limits
- labels
Every figure needs the title
37 / 43
Interactive graphics
39 / 43
Generative art
41 / 43