Lab 04 Solution
This lab exercise is due 23:59 Wednesday 7 April (NZST).
- You should submit an R file (i.e. file extension
.R) containing R code that assigns the appropriate values to the appropriate symbols. - Your R file will be executed in order and checked against the values that have been assigned to the symbols using an automatic grading system. Marks will be fully deducted for non-identical results.
- Intermediate steps to achieve the final results will NOT be checked.
- Each question is worth 0.2 points.
- You should submit your R file on Canvas.
- Late assignments are NOT accepted unless prior arrangement for medical/compassionate reasons.
In this lab exercise, you are going to work with two data sets:
step-count.csv that contains Dr Wang’s hourly step counts, and
location.csv with cities where she was in 2019. You shall use the
following code snippet (and include them upfront in your R file) to
start with this lab session:
library(tidyverse)
step_count_raw <- read_csv("data/step-count/step-count.csv",
locale = locale(tz = "Australia/Melbourne"))
location <- read_csv("data/step-count/location.csv")
step_count_raw
#> # A tibble: 5,448 x 3
#> `Date/Time` Date `Step Count (count)`
#> <dttm> <date> <dbl>
#> 1 2019-01-01 09:00:00 2019-01-01 764
#> 2 2019-01-01 10:00:00 2019-01-01 913
#> 3 2019-01-02 00:00:00 2019-01-02 9
#> 4 2019-01-02 10:00:00 2019-01-02 2910
#> 5 2019-01-02 11:00:00 2019-01-02 1390
#> 6 2019-01-02 12:00:00 2019-01-02 1020
#> 7 2019-01-02 13:00:00 2019-01-02 472
#> 8 2019-01-02 15:00:00 2019-01-02 1220
#> 9 2019-01-02 16:00:00 2019-01-02 1670
#> 10 2019-01-02 17:00:00 2019-01-02 1390
#> # … with 5,438 more rows
location
#> # A tibble: 21 x 2
#> date location
#> <date> <chr>
#> 1 2019-01-15 Austin
#> 2 2019-01-16 Austin
#> 3 2019-01-17 Austin
#> 4 2019-01-18 Austin
#> 5 2019-01-19 Austin
#> 6 2019-01-20 Austin
#> 7 2019-01-21 Austin
#> 8 2019-01-22 Austin
#> 9 2019-01-23 Austin
#> 10 2019-01-24 Austin
#> # … with 11 more rows
Suppose that you have created an Rproj for this course. You need to
download step-count.csv
here
and location.csv
here,
to data/step-count/ under your Rproj folder.
- You’re required to use relative file paths
data/step-count/step-count.csvanddata/step-count/location.csvto import these data. - NO marks will be given for using URL links or different file paths.
- DO NOT include
install.packages()in your R file. - DO NOT print any R objects and plots.
Question 1
Change the column names of step_count_raw to date_time, date, and
count. You should end up with a tibble called step_count.
step_count <- step_count_raw %>%
rename(
date_time = `Date/Time`,
date = Date,
count = `Step Count (count)`
)
step_count
#> # A tibble: 5,448 x 3
#> date_time date count
#> <dttm> <date> <dbl>
#> 1 2019-01-01 09:00:00 2019-01-01 764
#> 2 2019-01-01 10:00:00 2019-01-01 913
#> 3 2019-01-02 00:00:00 2019-01-02 9
#> 4 2019-01-02 10:00:00 2019-01-02 2910
#> 5 2019-01-02 11:00:00 2019-01-02 1390
#> 6 2019-01-02 12:00:00 2019-01-02 1020
#> 7 2019-01-02 13:00:00 2019-01-02 472
#> 8 2019-01-02 15:00:00 2019-01-02 1220
#> 9 2019-01-02 16:00:00 2019-01-02 1670
#> 10 2019-01-02 17:00:00 2019-01-02 1390
#> # … with 5,438 more rows
Question 2
Join the second data location to the primary data step_count. You
should end up with a tibble called step_count_loc.
step_count_loc <- step_count %>%
left_join(location)
step_count_loc
#> # A tibble: 5,448 x 4
#> date_time date count location
#> <dttm> <date> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 2019-01-01 09:00:00 2019-01-01 764 <NA>
#> 2 2019-01-01 10:00:00 2019-01-01 913 <NA>
#> 3 2019-01-02 00:00:00 2019-01-02 9 <NA>
#> 4 2019-01-02 10:00:00 2019-01-02 2910 <NA>
#> 5 2019-01-02 11:00:00 2019-01-02 1390 <NA>
#> 6 2019-01-02 12:00:00 2019-01-02 1020 <NA>
#> 7 2019-01-02 13:00:00 2019-01-02 472 <NA>
#> 8 2019-01-02 15:00:00 2019-01-02 1220 <NA>
#> 9 2019-01-02 16:00:00 2019-01-02 1670 <NA>
#> 10 2019-01-02 17:00:00 2019-01-02 1390 <NA>
#> # … with 5,438 more rows
sum(is.na(step_count_loc$location))
#> [1] 5125
Question 3
Replace missing values with "Melbourne" in the location column of
the step_count_loc. You should end up with a tibble called
step_count_full.
# NO mark given to Q2, if you do the following line:
# step_count_loc$location[is.na(step_count_loc$location)] <- "Melbourne"
step_count_full <- step_count_loc %>%
mutate(location = case_when(
is.na(location) ~ "Melbourne",
TRUE ~ location))
step_count_full
#> # A tibble: 5,448 x 4
#> date_time date count location
#> <dttm> <date> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 2019-01-01 09:00:00 2019-01-01 764 Melbourne
#> 2 2019-01-01 10:00:00 2019-01-01 913 Melbourne
#> 3 2019-01-02 00:00:00 2019-01-02 9 Melbourne
#> 4 2019-01-02 10:00:00 2019-01-02 2910 Melbourne
#> 5 2019-01-02 11:00:00 2019-01-02 1390 Melbourne
#> 6 2019-01-02 12:00:00 2019-01-02 1020 Melbourne
#> 7 2019-01-02 13:00:00 2019-01-02 472 Melbourne
#> 8 2019-01-02 15:00:00 2019-01-02 1220 Melbourne
#> 9 2019-01-02 16:00:00 2019-01-02 1670 Melbourne
#> 10 2019-01-02 17:00:00 2019-01-02 1390 Melbourne
#> # … with 5,438 more rows
step_count_full %>%
slice(90:95)
#> # A tibble: 6 x 4
#> date_time date count location
#> <dttm> <date> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 2019-01-14 17:00:00 2019-01-14 65.7 Melbourne
#> 2 2019-01-14 19:00:00 2019-01-14 22 Melbourne
#> 3 2019-01-14 20:00:00 2019-01-14 1 Melbourne
#> 4 2019-01-15 03:00:00 2019-01-15 8 Austin
#> 5 2019-01-15 05:00:00 2019-01-15 355 Austin
#> 6 2019-01-15 06:00:00 2019-01-15 1800 Austin
Question 4
Aggregate the hourly data step_count_full to daily step counts. You
should end up with a tibble called step_count_daily.
step_count_daily <- step_count_full %>%
group_by(date) %>%
summarise(daily_count = sum(count))
step_count_daily
#> # A tibble: 364 x 2
#> date daily_count
#> <date> <dbl>
#> 1 2019-01-01 1677
#> 2 2019-01-02 14987
#> 3 2019-01-03 9424
#> 4 2019-01-04 9
#> 5 2019-01-05 7359
#> 6 2019-01-06 21
#> 7 2019-01-07 9057.
#> 8 2019-01-08 10341
#> 9 2019-01-09 6394
#> 10 2019-01-10 7489
#> # … with 354 more rows
Question 5
Subset step_count_daily with daily counts that are greater than or
equal to 10,000 steps. You should end up with a tibble called
step_count_10000.
step_count_10000 <- step_count_daily %>%
filter(daily_count >= 10000)
step_count_10000
#> # A tibble: 108 x 2
#> date daily_count
#> <date> <dbl>
#> 1 2019-01-02 14987
#> 2 2019-01-08 10341
#> 3 2019-01-22 15579
#> 4 2019-01-23 15362
#> 5 2019-01-31 11287.
#> 6 2019-02-15 10117
#> 7 2019-02-21 10312
#> 8 2019-02-26 12005
#> 9 2019-03-01 14510
#> 10 2019-03-05 11754.
#> # … with 98 more rows
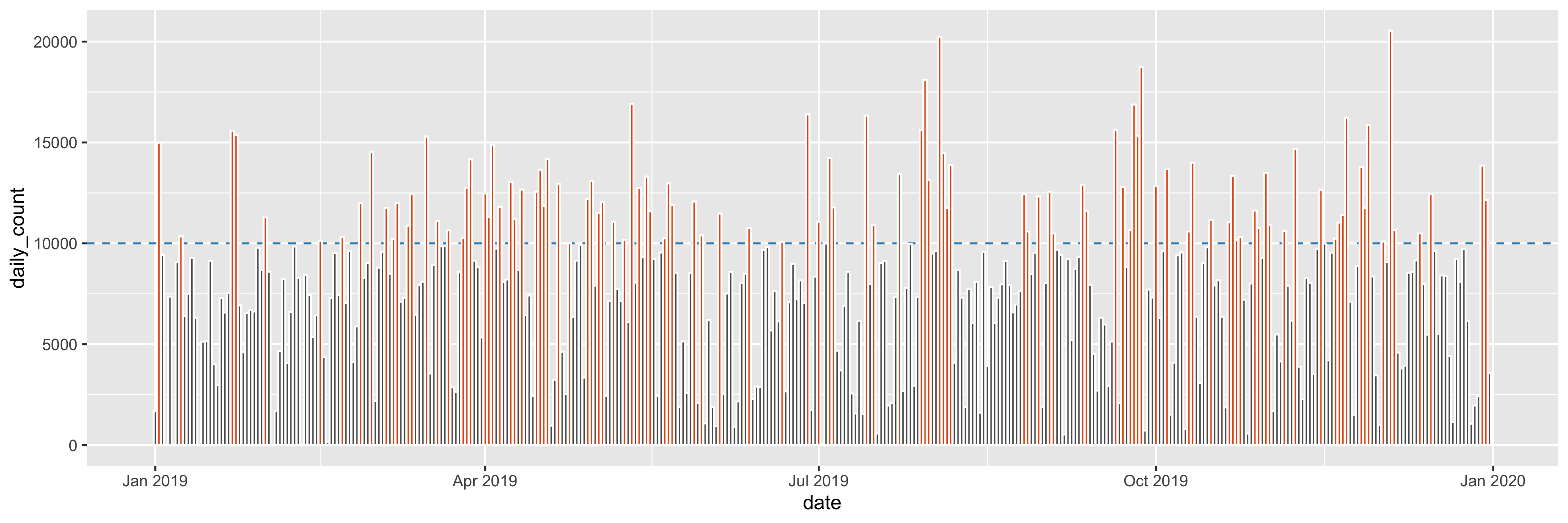
Question4fun (NO marks)
Plot daily counts over the year of 2019 and highlight these daily counts that are greater than or equal to 10,000.
- horizon line:
colour = "#2b8cbe", andlinetype = "dashed" - bar:
fill = "#e6550d", andcolour = "white"
step_count_daily %>%
ggplot(aes(date, daily_count)) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 10000, colour = "#2b8cbe", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_col(colour = "white") +
geom_col(data = step_count_10000, fill = "#e6550d", colour = "white")